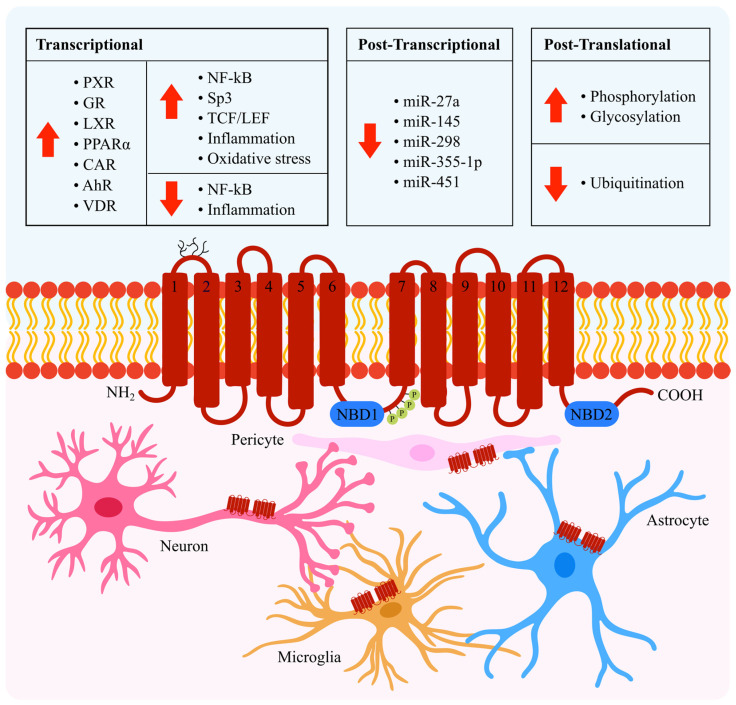
Figure 1.
Structure, location and regulation of P-gp in the brain. The P-gp protein consists of two transmembrane domains, each comprising six membrane-spanning helices, and two intracellular ATP-binding regions (nucleotide-binding domains; NBDs). Phosphorylation sites (serine residues S661, S667, S671 and S683 [6]), depicted by green circles, are located within the linker region connecting the two domains. Glycosylation of P-gp occurs at the asparagine residues N91, N94 and N99 [6], depicted by branched lines between transmembrane helices 1 and 2. In the brain, P-gp is expressed on the luminal surface of BBB endothelial cells. Here, its mRNA and protein expression and activity levels are up- or downregulated by a range of transcription factors, miRNAs and post-translational mechanisms. The expression of P-gp protein has additionally been identified in pericytes, astrocytes [7,8], neurons [7,9] and microglia [10] of the brain.