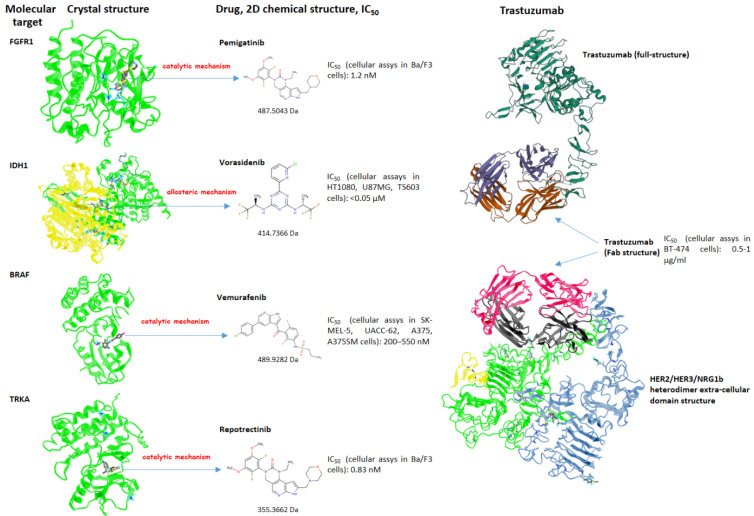
Figure 5.
Schematic representation of the molecular targets and their crystal structures, inhibitory small molecules with their 2D chemical structures, molecular weights, and IC50 (for each IC50, the cellular model used to establish it is reported). For exploring the single amino acids involved in the structural interactions between the chemical compounds and the molecular target in a 3D navigation perspective, please visit the online research tool of the NCBI (National Center for Biotechnology Information) [87]. When the crystal structure of the protein in the complex with the molecule reported in the article was not available, we reported the structure bounded to a chemical compound belonging to the same functional class (vorasidenib for ivosidenib and repotrectinib for larotrectinib, both interacting with the same functional regions of IDH1 and TRKA, respectively). The inhibitory effect through the “allosteric mechanism” signifies that the molecule inhibits the target by binding to an allosteric site that is distant from the catalytic/active site of the kinase. In this case, a conformational change is induced, preventing access to the enzymatic pocket.