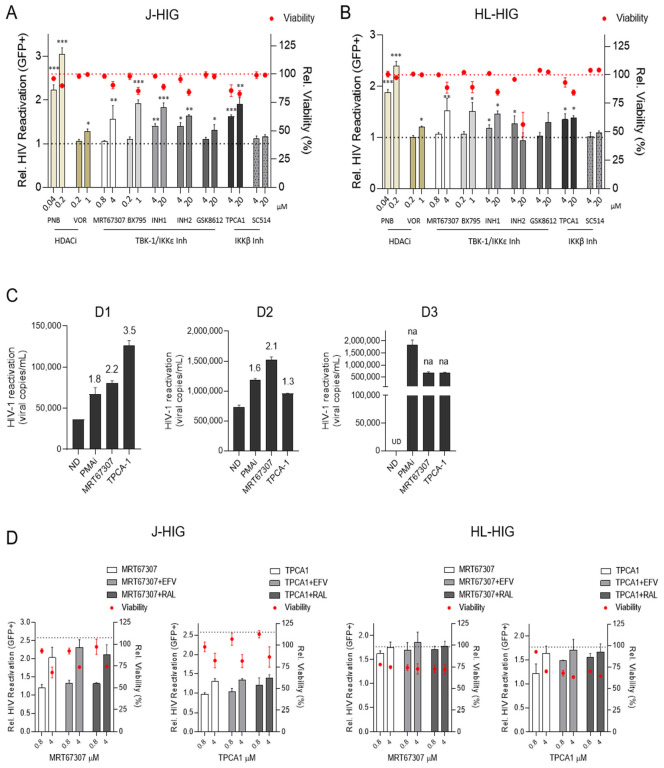
Figure 1.
IKK Inhibitors induce HIV reactivation in in vitro and ex vivo models of latency. (A) HIV reactivation induced by IKKis in latently infected lymphoid Jurkat (J-HIG) and (B) myeloid HL-60 (HL-HIG) cells. The activity of IKKis MRT67307, TPCA-1, BX795, Inh 1, Inh2, GSK8612 and SC514 was determined by the quantification of GFP+ cells (%) after culturing J-HIG or HL-HIG cells with IKKis for 24 h. HDCAi panobinostat (PNB) and vorinostat (VOR) were used as controls for HIV-1 reactivation. Basal reactivation (grey-dashed line) in J-HIG and HL-HIG was established according to the no-drug condition (ND). Toxicity of IKKis (red-dashed line) in J-HIG and HL-HIG cells was measured as percentage of viable cells (LIVE/DEAD™ staining) by flow cytometry related to the ND condition. (C) Ex vivo viral reactivation capacity of IKKis in CD4+ T cells from HIV+ individuals. HIV-RNA copies were determined in the cell culture supernatant from HIV+ CD4+ T cells incubated for 72 h with 4 µM of MRT67307 or TPCA-1. PMA/ionomycin (50 ng/mL/1 µM, PMAi) was used as the positive control of HIV-1 reactivation. Fold-change (FC) relative to ND are indicated above each bar for the respective treatment conditions. FC values, if not available (na) because of undetermined RT-qPCR ct values (UD), are highlighted in the chart. (D) HIV-1 reactivation capacity of IKKis in the presence of antiretroviral drugs. Reactivation ability of MRT67307 (4 µM) and TPCA-1 (4 µM) is not affected by the ART (efavirenz, EFV at 0.3 µM or raltegravir, RAL at 2.2 µM), neither in latently infected lymphoid J-HIG (left panel) nor myeloid HL-HIG cells (right panel). Viral reactivation was measured 24 h after incubation with the corresponding conditions. The grey-dashed line indicates reactivation in the PMAi control. Red dots indicate relative cell viability. Mean ± SD of three independent experiments is shown. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001.