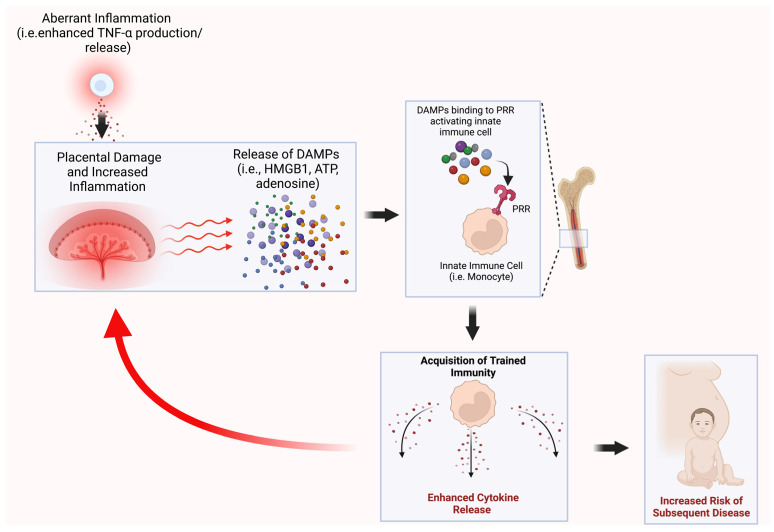
Figure 2.
Potential mechanism linking the acquisition of trained immunity after exposure to aberrant maternal inflammation to an increased risk of disease. We hypothesize that the aberrant maternal inflammation associated with pregnancy complications results in the acquisition of trained immunity (TI) in mothers and their offspring, and that this TI mediates the increased risk of adverse health outcomes in subsequent generations. DAMPs—damage-associated molecular patterns; HMGB1—high-mobility group box 1; ATP—adenosine triphosphate; PRR—pattern recognition receptor.