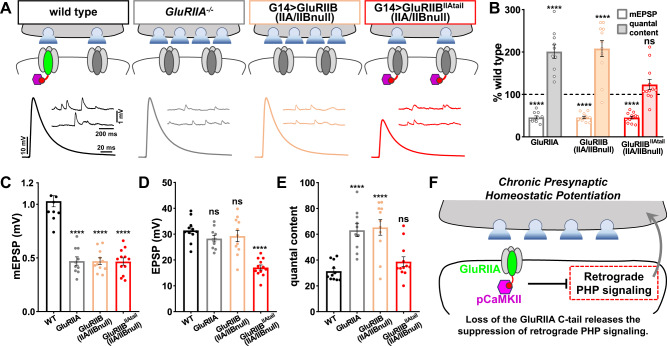
Fig. 8. Retrograde PHP signaling is occluded when pCaMKII is recruited to NMJs lacking GluRA receptors.
Α Schematic and representative traces illustrating that retrograde PHP signaling is occluded at NMJs containing chimeric GluRB receptors, while PHP is robustly expressed at NMJs containing wild-type GluRB receptors. Note that while mEPSP amplitudes are similarly reduced at NMJs containing only GluRB receptors, the presynaptic release does not increase when pCaMKII is recruited to NMJs by chimeric GluRB receptors. B Quantification of mEPSP and quantal content values in the indicated genotypes normalized to wild-type values (wild type: n = 12; GluRIIA−/−, n = 10, p < 0.0001 for mEPSP, p < 0.0001 for QC; G14 > GluRIIB: n = 11, p < 0.0001 for mEPSP, p < 0.0001 for QC; G14 > GluRIIBIIAtail: n = 12, p < 0.0001 for mEPSP, p = 0.4908 for QC). C–E Quantification of average mEPSP amplitude (C), EPSP amplitude (D), and quantal content values (E) in the indicated genotypes (wild type: n = 12; GluRIIA−/−, n = 10, p < 0.0001 for mEPSP, p = 0.331 for EPSP, p < 0.0001 for QC; G14 > GluRIIB: n = 11, p < 0.0001 for mEPSP, p = 0.596 for EPSP, p < 0.0001 for QC; G14 > GluRIIBIIAtail: n = 12, p < 0.0001 for mEPSP, p < 0.0001 for EPSP, p = 0.490 for QC). Repeated measures one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test with a significance value of 0.05. p Value adjusted for multiple comparisons. F Schematic summarizing that active pCaMKII is lost from postsynaptic compartments due to the physical absence of the GluRIIΑ C-tail. This, in turn, releases the inhibition of retrograde PHP signaling. Error bars indicate ±SEM. ****p < 0.0001; ns, not significant. n values indicate biologically independent NMJs. Absolute values for normalized data are summarized in Table S1. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.