FIGURE 3.
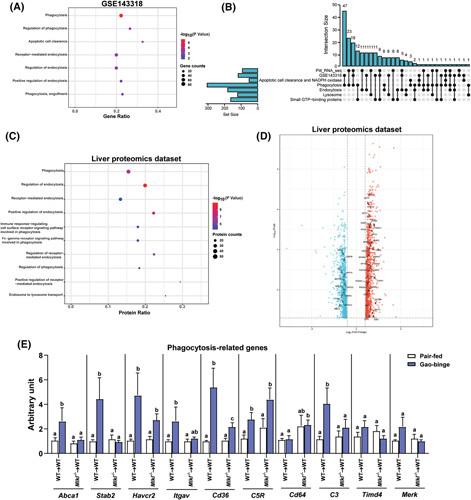
Bioinformatic analysis of liver RNA‐sequencing and proteomics data from patients with alcohol‐associated hepatitis (AH) and effect of mixed lineage kinase domain‐like pseudokinase (Mlkl) deficiency in myeloid cells on expression of phagocytosis‐related genes in liver in response to ethanol. (A) Gene ontology biological process (GO‐BP) enrichment analysis was performed based on differentially expressed genes (DEGs) involved in intracellular vesicle trafficking pathways between healthy controls (HC; n = 5) and patients with severe AH (sAH; n = 5) in GSE143318 dataset. (B) An upset plot visualized the intersection between DEGs enriched in intracellular vesicle trafficking in HC and patients with sAH from Pitt_RNA_seq and GSE143318 datasets and genes in multiple GO‐BP classes and key protein systems, including apoptotic cell clearance, phagocytosis, lysosome, small guanosine triphosphate (GTP)‐binding proteins, and NADPH oxidase. (C) GO‐BP enrichment analysis was performed based on differentially expressed proteins (DEPs) involved in intracellular vesicle trafficking pathways between HC (n = 12) and patients with sAH (n = 6) in the global proteomics dataset.22 (D) The volcano plot revealed upregulated and downregulated proteins that were enriched in intracellular vesicle trafficking in the proteomics dataset.22 (E) Expression of messenger RNA (mRNA) for phagocytic genes including ATP binding cassette subfamily A member (Abca1), stabilin (Stab2), hepatitis A virus cellular receptor (Havcr2), intergrin subunit alpha V (Itgav), Cd36, C5r, Cd64, C3, T cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain containing (Timd4), and MER proto‐oncogene, tyropsine kinase(Merk) in livers from wild‐type (WT)→WT and Mlkl −/− →WT mice was assessed by quantitative real‐time polymerase chain reaction and normalized to 18S ribosomal RNA. n = 4–6. Values represent means ± SEM; values for each mRNA with different superscripts are significantly different from each other; p < 0.05.
