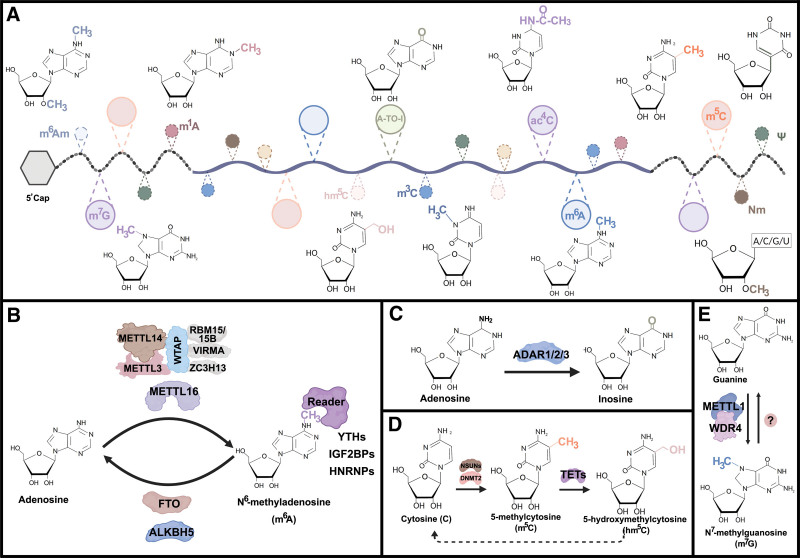
Figure 1.
The covalent chemical modifications in mRNA. (A) A schematic view of chemical structures of RNA modifications (m6Am, m1A, A-to-I, ac4C, m5C, Ψ, m6A, hm5C, m3C, m7G and Nm) in mRNA. (B) The regulation of m6A by “writers,” “erasers,” and “readers.” The m6A modification is installed by writers, multicomponent m6A MTC (composed of METTL3, METTL14, WTAP, RBM15/15B, KIAA1429, and ZC3H13) or METTL16 alone. The two demethylases (eraser), FTO and ALKBH5, remove m6A modifications. The m6A residue is recognized by the three main classes, including the YTH domain family, IGF2BP family and HNRP family. (C) ADAR enzymes catalyze the A-to-I hydrolytic deamination reaction. (D) The NSUN methyltransferases and DNMT2 catalyze methylation of cytosine-5 and TET family function as dioxygenases catalyzing m5C to hm5C. (E) The formation of m7G is catalyzed by methyltransferases complex, which is composed of METTL1 and WDR4. ADAR = adenosine deaminases acting on RNA.