Figure 6. ACVR1 mutations confer oncogenic BMP signalling in H3.1K27M HGG.
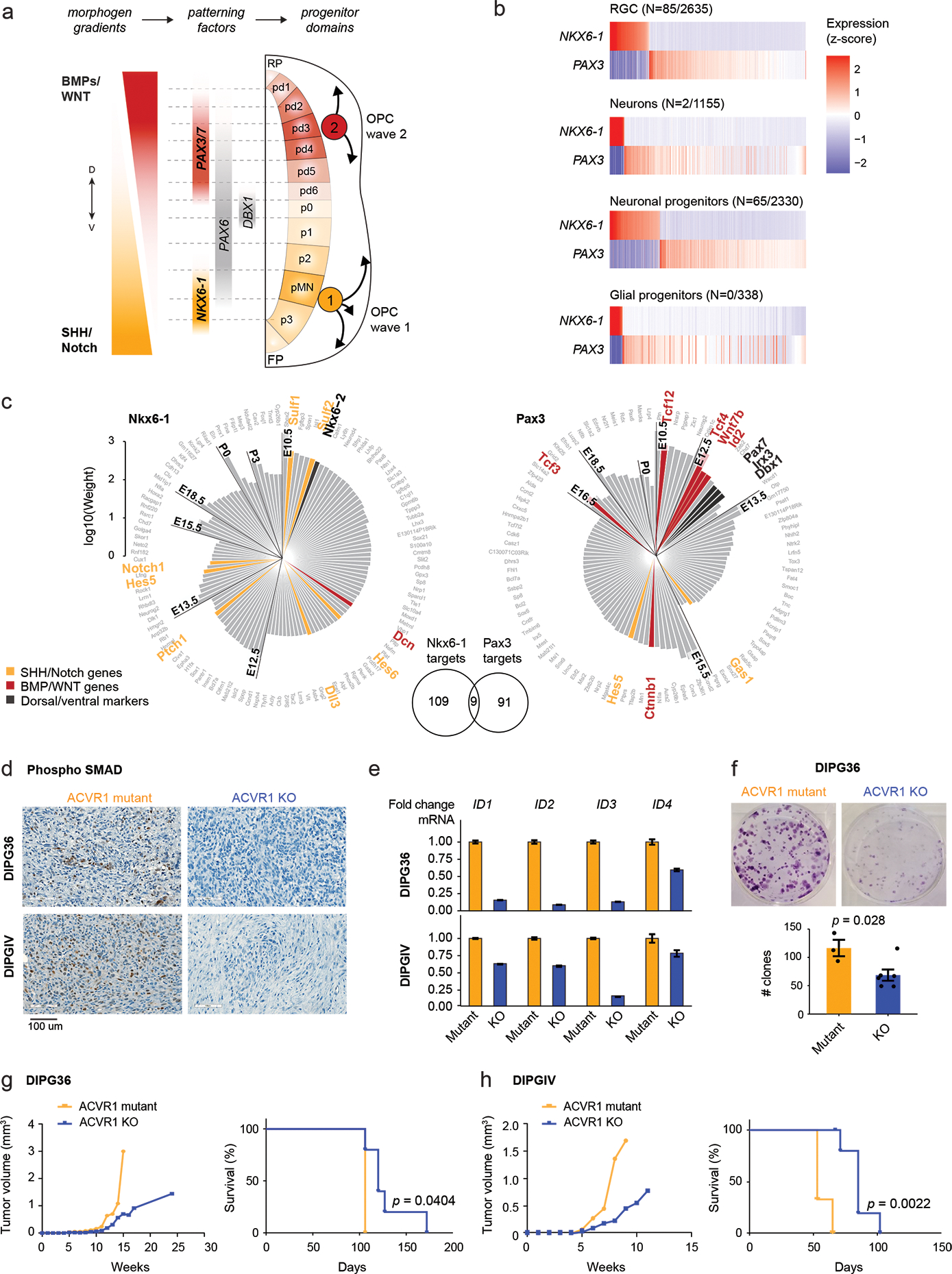
a. Schematic of coronal section of the developing hindbrain/neural tube, depicting ventral (V; NKX6-1+) and dorsal (D; PAX3+) waves of oligodendrocyte generation during development. RP, roof plate. pd, dorsal progenitor domain. p, ventral progenitor domain. pMN, progenitor of motor neurons domain. FP, floor plate.
b. Scaled scRNAseq expression (Z-score across cells) of NKX6-1 and PAX3 in cell types of the normal human fetal hindbrain (N=79,428 cells, 11 donors), showing their expression is largely mutually exclusive. The number of cells where both NKX6-1 and PAX3 are detected out of the total number NKX6-1+ or PAX3+ cells of the cell type is indicated in parentheses.
c. Targets of NKX6-1 and Pax3 extracted from gene regulatory networks inferred from scRNAseq data of E10-P6 mouse pons. Each bar represents one target, and the height of the bar represents the edge weight between the TF and the target. Targets are plotted clockwise from top, in order of the earliest time point at which they are detected as a target.
d. Immunohistochemistry staining of phosphorylated SMAD in mouse xenografts from the H3.1K27M DIPG cell lines DIPG36 and DIPGIV. Left: ACVR1 mutant line, right: isogenic cell line with CRISPR-based removal of ACVR1.
e. ddPCR for ID genes in DIPG36 and DIPGIV ACVR1 mutant and ACVR1 KO lines. Data are represented as the fold change +/− SD, based on N=3 technical replicates per cell line per condition.
f. Clone-formation assay for DIPG36 (ACVR1 mutant) and isogenic ACVR1 KO lines (ACVR1 mutant, N=3 biological replicates; ACVR1 KO, N=6; p-value = 0.028, 2-tailed t-test). Error bars represent mean values +/− SEM.
g-h. Tumor volume evolution and survival of mouse xenograft cohorts generated from DIPG36 (ACVR1 mutant, N=3 mice; ACVR1 KO, N=5 mice; p-value = 0.0404, log-rank test) and DIPGIV (ACVR1 mutant, N=3 mice; ACVR1 KO, N=6 mice; p-value = 0.0022, log-rank test).
