Figure 4. NFκB is induced with age, binds to the MR P1 and P2 promoters in response to oxidative stress, and regulates expression of both MR isoforms in human aortic smooth muscle cells (HASMC).
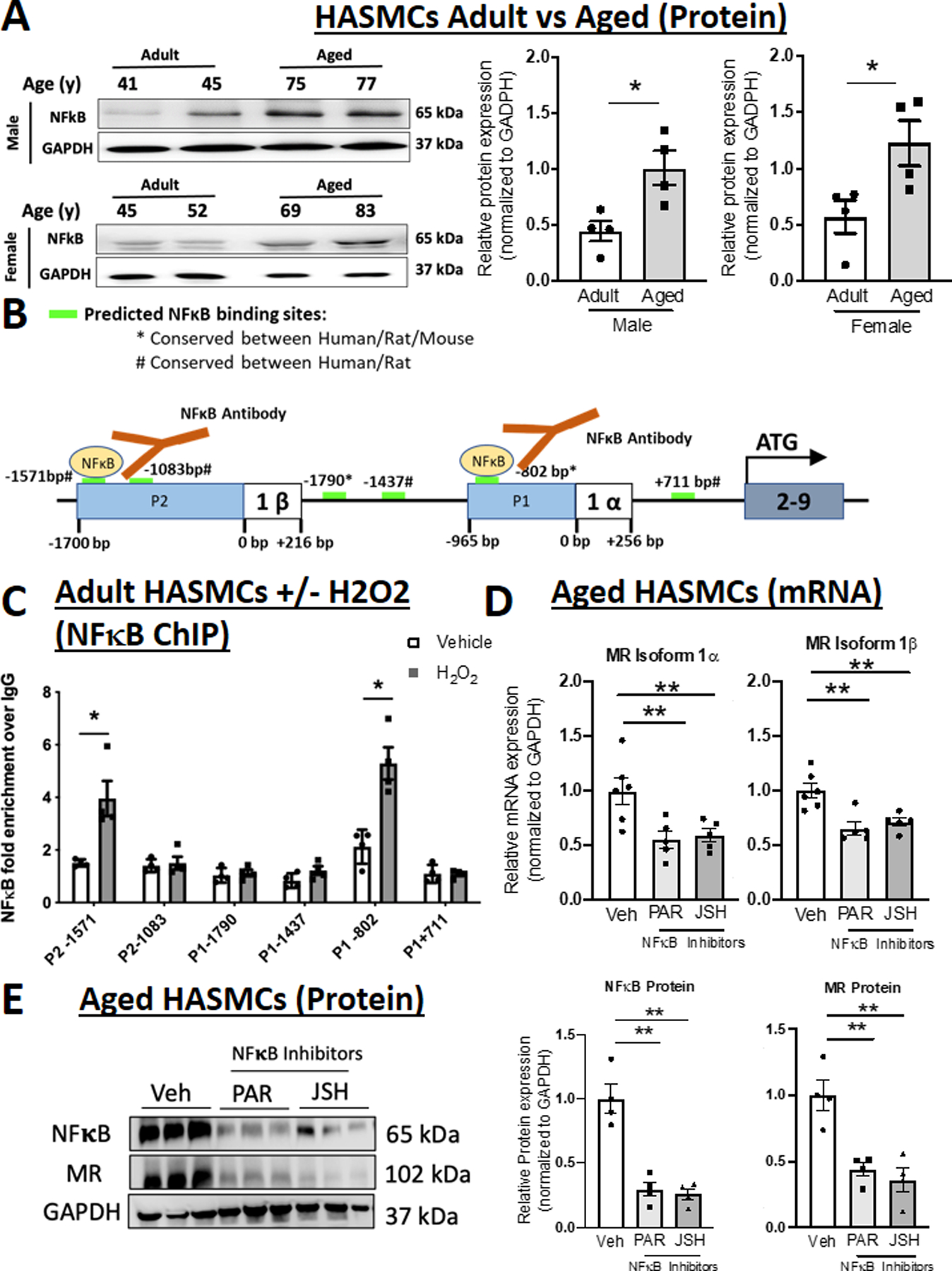
(A) Representative immunoblots and quantification of NFκB protein expression comparing primary HASMC from adult (average age 40s) versus aged (average age late 70s) male and female donors. N=4 for each sex and age group. (B) Schematic representation of the six predicted NFκB binding sites (green bars) conserved between human and rodents (rat and/or mouse). (C) Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) performed in chromatin isolated from HASMCs treated with vehicle (white bar) or H2O2 (grey bar) for 24 hours using anti-NFκB antibody compared to control IgG antibody and PCR with primers specific to the predicted P1 and P2 promoter NFκB binding sites. N=4 experiments. (D) Quantification of MR mRNA isoforms in aged primary HASMCs treated with two distinct NFκB inhibitors Parthenolide (PAR) and JSH23 (JSH). N=5 experiments. (E) Representative immunoblots and quantification of NFκB and MR protein expression in aged primary HASMCs treated with NFκB inhibitors. N=4. Dot plots show the individual data points and bars indicate the mean with error bars indicating the SEM. One-way ANOVA with Tukey post hoc test, **p<0.01.
