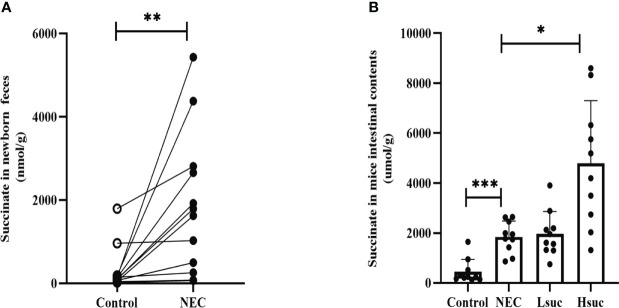
Figure 1.
The levels of intestinal succinate were increased in both human neonates and mouse pups with NEC. Succinate levels (A) in feces from control and NEC human neonates (n=12 per group), and (B) in mouse intestinal contents from four independent groups (n=10 per group). Statistical analysis was performed with paired t-test or one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s posttest. Bars in the graph represent the mean ± SD, and significant differences are shown by *P <0.05, **P <0.01, ***P <0.001. NEC, necrotizing enterocolitis; Lsuc, mice with NEC receiving 50 mM succinic acid intervention; Hsuc, mice with NEC receiving 100 mM succinic acid intervention.