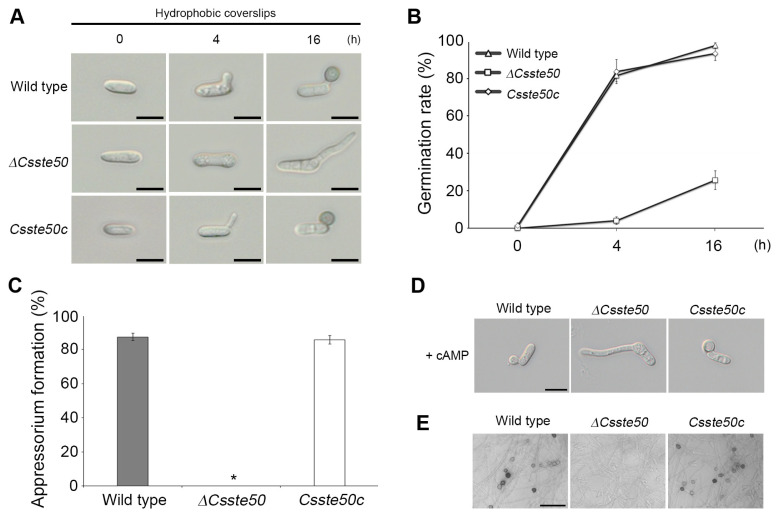
Fig. 5.
Conidial germination and appressorium formation of the ΔCsste50 on the hydrophobic surface. (A) Visualization of appressorium formation. Conidial drops (5 × 104 conidia/ml) were placed on the hydrophobic surface of coverslips and photographed at 0, 4, and 16 h post-inoculation. Scale bars = 10 μm. (B, C) Quantitative measurements of conidial germination and appressorium formation. A minimum of 100 conidia were examined to assess the conidial germination rate at 0, 4, and 16 h post-inoculation (B) and appressorium formation rate at 16 h post-inoculation (C). The asterisk (*) indicates a complete defect in appressorium formation of ΔCsste50. (D) Recovery of appressorium formation with exogenous treatment of cAMP. The cAMP (5 mM) was added to the conidial drops at 2 h post-inoculation. Photographs were taken at 16 h post-inoculation. Scale bar = 10 μm. (E) Visualization of appressorium like structure (ALS) formation. Mycelial agar plugs grown on 5-day-old oatmeal agar were placed on glass slides and covered with coverslips. Photographs were taken at 72 h post-inoculation. All experiments were conducted in triplicate and repeated three times. Scale bar = 30 μm.