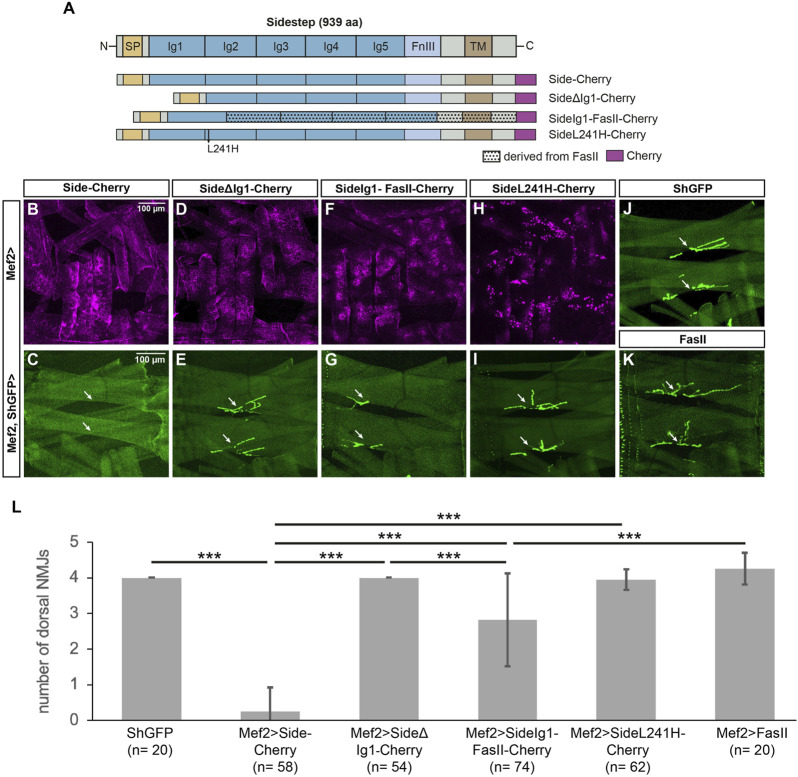
FIGURE 3.
The first Ig domain of Side is necessary and partially sufficient to attract motor axons. (A) Scheme of the domain structure of Sidestep and various Cherry-fusion proteins used in the study. SideΔIg1 lacks the first Ig domain, and SideIg1-FasII replaces the first Ig domain in FasII with the first Ig domain of Side. The positions of the L241H point mutation and the Cherry tags (magenta) are indicated. aa, amino acids; SP, signal peptide; Ig, immunoglobulin domain; FnIII, fibronectin type-III domain; TM, transmembrane domain. FasII, Fasciclin II. Not to scale. (B, D, F, H) Confocal images of undissected third instar larvae expressing the indicated Cherry-fusion proteins in muscles under control of Mef2-Gal4. Depicted is the lateral muscle field showing the distribution of the fusion proteins in transverse muscles M21-24 (center, other muscles are also visible). (C, E, G, I–K) Confocal images of undissected ShGFP larvae showing that ectopic expression of Side-Cherry in muscles prevents NMJ formation on dorsal-most muscles 1/9 and 2/10 (C, arrows). Replacing the first Ig domain of FasII with the first Ig domain of Side disturbed dorsal NMJs in size and position (G, arrows). Compared to ShGFP controls (J), expression of SideΔIg1 (E), SideL241H (I) or FasII (K) had no effect. Scale bar: 100 µm. (L) Quantification of the number of NMJs on the dorsal-most muscle pairs 1/9 and 2/10 in the indicated genotypes. ShGFP control animals have four NMJs in this region, one major structure per muscle fiber. n, number of hemisegments; statistical significance was calculated using two-tailed Mann–Whitney-U-test: ***, p < 0.001.