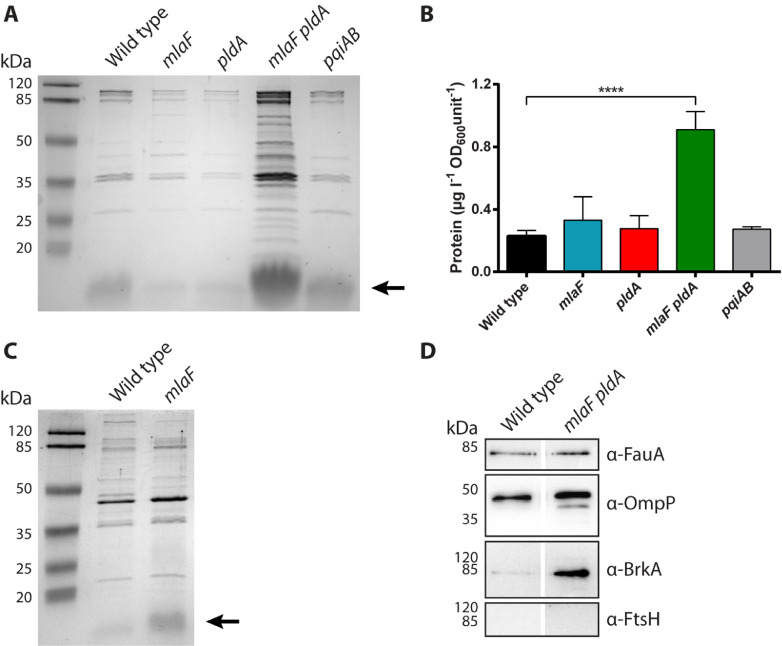
Fig. 4.
Influence of disrupted lipid asymmetry on OMV production. (A) B. pertussis strain B213 and its mutant derivatives were grown for two days in Verwey medium in Erlenmeyer flasks after which OMVs were isolated. OMVs released from equal amounts of cells, based on OD600, were analyzed by SDS-PAGE. Proteins were stained with the Bradford reagent. The reagent also stains LPS, which is indicated with an arrow on the right. (B) Isolated OMVs were quantified based on protein content using a Lowry assay, and quantities are expressed as amount of protein per liter of bacterial culture per OD600 unit. Graph shows mean values with standard deviations from three independent experiments. Statistical significance was determined by one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett's multiple comparisons test using GraphPad Prism 6 and is indicated by asterisks (****, p < 0.0001). (C) OMV production by B. bronchiseptica strain BB-D09-SR and its mlaF mutant derivative was assessed by SDS-PAGE as described for panel A. LPS (lipid A plus core moiety) is indicated with an arrow. (D) OMVs from B. pertussis strain B213 and its mlaF pldA mutant derivative were equally loaded, based on protein content, and analyzed by Western blotting using antisera directed against OMPs FauA (78 kDa), OmpP (39 kDa), BrkA (73 kDa), and inner-membrane protein FtsH (69 kDa) as indicated at the right. In panels A, C, and D, the positions of molecular weight standard proteins are indicated at the left.