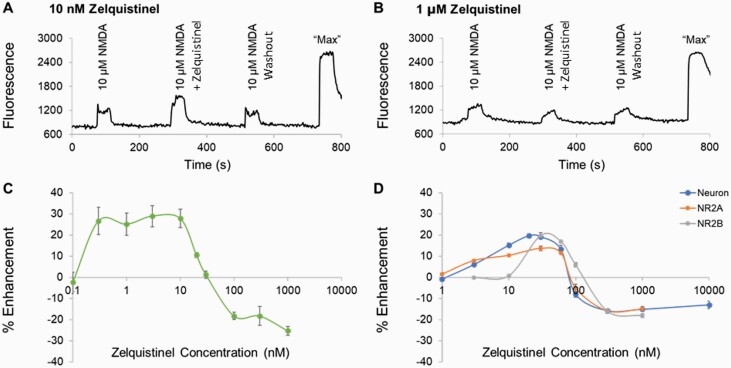
Figure 1.
Zelquistinel potentiated NMDA- or glutamate-induced changes in intracellular calcium. Zelquistinel potentiated NMDA-induced intracellular calcium ([Ca2+]i) changes in rat cortical neurons and in HEK293 cells expressing NR2A or NR2B receptors. Representative traces showing (A) the potentiation effect of 10 nM zelquistinel and (B) the inhibition effect of 1 μM zelquistinel. (C) Dose-dependent effects of zelquistinel on NMDA alone (10 µM) induced [Ca2+]i response (n = 4–8 coverslips for each data point). (D) Dose-dependent effects of zelquistinel on [Ca2+]i changes in NR2A− (in the presence of 300 nM glutamate + 3 μM D-serine) or NR2B-expressing (in the presence of 100 nM glutamate+3 μM D-serine) HEK cells, or in cortical neurons (in the presence of 3 μM NMDA+3 μM D-serine; neuron) (n = 5–12 coverslips for each data point). Each point (C, D) represents mean ± SEM, and the percent enhancement is normalized to the signal induced by NMDA or glutamate only.