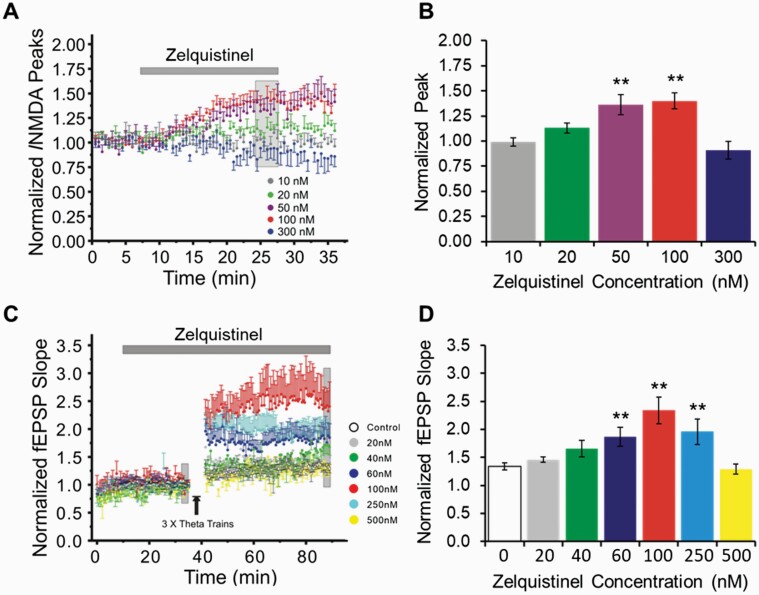
Figure 3.
Zelquistinel potentiated NMDAR-mediated excitatory postsynaptic currents and facilitated long-term potentiation in mPFC. (A, B) Zelquistinel potentiated NMDAR-mediated excitatory postsynaptic currents (EPSCs) in mPFC. (A) Time course of experiments comparing pharmacologically isolated NMDAR-mediated EPSCs (20–25 minutes after bath application of drug) with pre-drug baseline. (B) Zelquistinel concentration-dependently increased the magnitude of NMDAR-mediated EPSCs recorded from mPFC pyramidal neurons at 20, 50, and 100 nM concentrations; this effect was not observed at the higher concentration of 300 nM. *P < .01 vs pre-drug baseline in each cell via 1-way ANOVA with Bonferroni correction for multiple comparisons (n = 6–11). (C, D) Zelquistinel enhanced long-term potentiation (LTP) in mPFC. (C) Time course of experiments comparing LTP (of slices pretreated with 20–500 nM zelquistinel) induced by theta burst stimuli (TBS) with untreated slices (control, open circles). (D) Zelquistinel (60–250 nM) enhanced the magnitude of LTP. *P < .01 vs control (control [0 nM zelquistinel]) via Kruskal-Wallis 1-way ANOVA and Kruskal-Wallis multiple comparison Z-values test (n = 6–8 slices for each concentration tested).