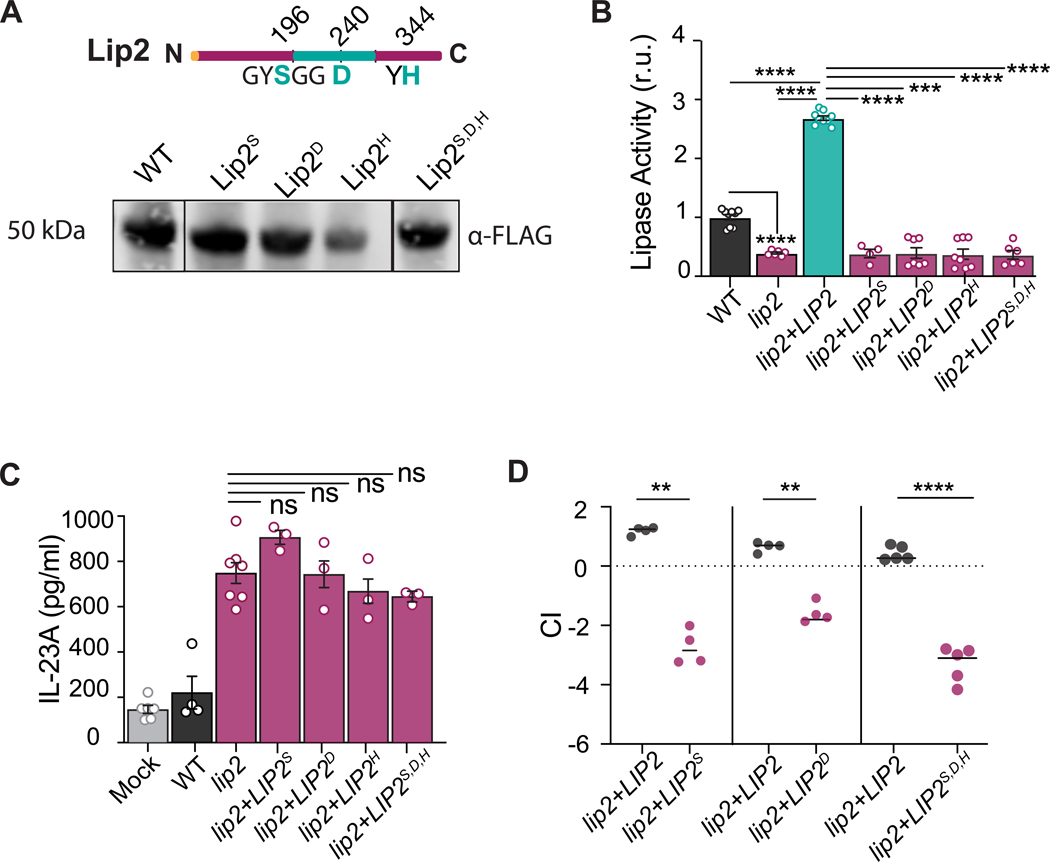
Figure 5. Predicted catalytic residues of Lip2 is required for its immunomodulatory role.
(A) Lip2 point mutant proteins are expressed. Cartoon of Lip2 protein domains (top). The lipase domain is represented by the green central region, with targeted residues of the predicted catalytic site also colored green. Immunoblot (bottom) of WT and point mutant alleles recovered from cell culture supernatants. Lip2 proteins are fused at the C-terminus to 6-His-FLAG (HHHHHHGGDYKDDDDK), and immunoblots were probed with anti-FLAG.
(B) Lip2 point mutants exhibit reduced lipase activity. Strains expressing the indicated allele of LIP2 were propagated to mid log growth (OD600=1) in liquid YEPD. Lipase assays were performed following a 10-minute incubation of supernatants with mixed lipids. Statistical significance between the different groups was determined by one-way ANOVA (Tukey’s multiple comparisons test); *** p<0.001; **** p<0.0001.
(C) Lip2 lipase activity is required to suppress the activation of BMDCs by C. albicans. Co-culture assays were performed with yeasts expressing WT Lip2 or the indicated Lip2 point mutants as in Figure 4D. Statistical significance between lip2 and the point-mutation mutants was determined by one-way ANOVA (Tukey’s multiple comparisons test); ns: 0.1964
(D) Lip2 lipase activity is required for virulence. BALB/c mice were infected with 1×105 CFU of a 1:1 mixture between lip2+LIP2 and either lip2+LIP2S196A, lip2+LIP2D240A, or lip2+LIP2S196A,D240A,H344A. Relative strain abundance in kidneys was determined by qPCR. Statistical significance between lip2+LIP2 and mutants was determined by a paired two-tailed t-test; **p < 0.01, ****p < 0.0001.