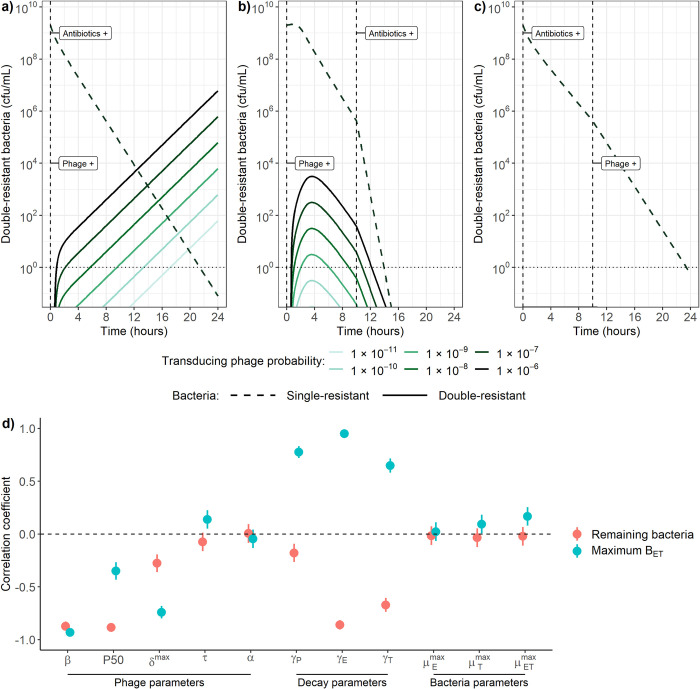
Fig 6. Sensitivity of phage-bacteria dynamics to changes in model parameters.
Effect of varying the transduction probability between 10−10 and 10−6 when a) antibiotics and phage are present at the start of the simulation, b) phage are present at the start, antibiotics are introduced 10h later, and c) antibiotics are present at the start, phage are added 10h later. Transduction probability is defined as the probability that a transducing phage carrying an AMR gene is released instead of a lytic phage during bacterial burst. The dashed lines for single-resistant bacteria overlap and cannot be distinguished. Vertical dashed lines indicate timing of addition of antibiotics or phage. cfu/mL: colony-forming units per mL. d) Partial rank correlation between model parameters, and remaining bacteria after 48h (pink) or maximum double-resistant bacteria (BET) concentration (blue). Information on the parameter ranges investigated can be found in Table 1. β: adsorption rate, P50: phage concentration at half saturation, δmax: burst size, τ: latent period, α: transduction probability, γP: phage decay, γE: erythromycin decay, γT: tetracycline decay, μmaxE: BE growth rate, μmaxT: BT growth rate, μmaxET: BET growth rate.