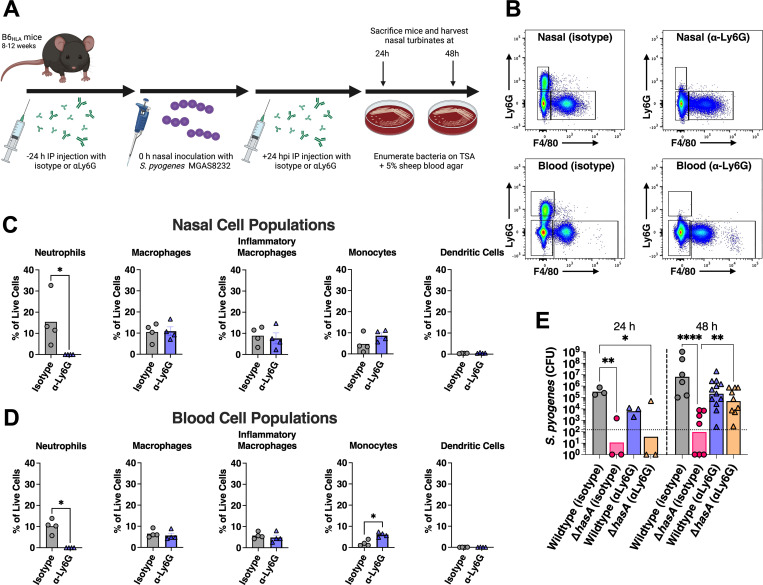
Fig 3. Early clearance of the HA capsule-deficient mutant from murine nasal turbinates is due to enhanced susceptibility to neutrophil-mediated killing.
(A) Schematic outline for in vivo depletion of neutrophils with injections of 250 μg (500 μg total) of αLy6G or isotype control rat IgG2a 24 h prior to and 24 h post-intranasal challenge with 108 CFUs of S. pyogenes wildtype or ΔhasA mutant strains. (B) Representative flow cytometric analyses of nasal and blood innate immune cells from the neutrophil depletion experiments at 48 h. Flow plots show live cells that were negative for CD4, CD45R and CD19, and gates were set on Ly6G+ and F4/80- cells for neutrophils, and Ly6G- and F4/80+ for macrophage populations. Percentage of innate immune cell populations from either nasal cell extracts (C) or blood (D) for the indicated treatment groups as percentage of live cells. Data points represent individual mice and the bars represent the mean. Significance was determined by Mann-Whitney test (*, P < 0.05) (E) Neutrophil effects on S. pyogenes survival in the nasopharynx. Data points represent CFUs from cNTs of individual mice 24 and 48 h post-infection. Horizontal bars represent the geometric mean. The horizontal dotted line indicates limit of detection. Significance was determined by two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ****, P < 0.0001). Fig 3A was created using Biorender.com.