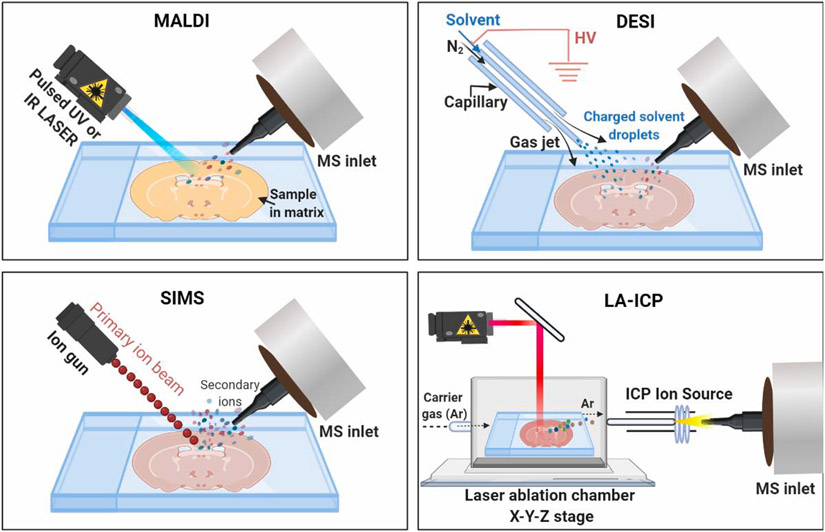
Fig. 2.
Schematic drawing of ion source of matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI), desorption electrospray ionization (DESI), secondary ion mass spectrometry (SIMS), and laser ablation inductively coupled plasma (LA-ICP) MSI. For MALDI-MSI analysis, the tissue section is coated with a thin layer of energy-absorbing matrix and irradiated by UV or IR laser pulses to desorb and release the ions of analyte. DESI-MSI is carried out by directing electrosprayed charged droplets and ions of solvent onto the surface of the tissue section; the impact of the charged particles produces gaseous ions of analyte. SIMS uses a beam of primary ions to irradiate the tissue surface and facilitate ionization by transferring energy from primary ions to the secondary ions of analyte. For LA-ICP-MSI analysis, tissue is placed in a chamber and ablated with laser; the laser induced sample particles are transported by a carrier gas and ionized in the plasma. After different ionization steps, the resulting ions are guided into the mass spectrometers for m/z analysis.