Figure 6.
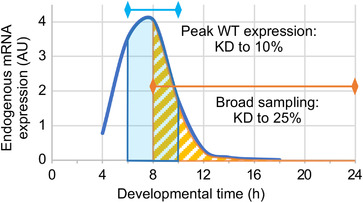
Tighter developmental staging mitigates underestimation of RNAi knockdown when assayed with a nested qPCR amplicon. This schematized representation based on empirical data for Tc‐zen1 illustrates how the time window assayed by RT‐qPCR compares to the time course of endogenous expression,[ 20 ] and in turn how this affects the apparent efficiency of RNAi knockdown (KD). Even with a nested amplicon, which detects both endogenous mRNA and dsRNA, assays that strictly target the time window of peak endogenous expression document strong RNAi knockdown (blue: based on use of Fragment 3 depicted in Figure 1A; ref. [20]). In contrast, broad sampling that includes periods of low endogenous expression is more susceptible to underestimation of knockdown (orange: to 25% of wild type levels, based on Fragment 2, data in Figure 1B). This is because total RNA from broadly staged samples has a higher proportion of dsRNA relative to endogenous mRNA.
