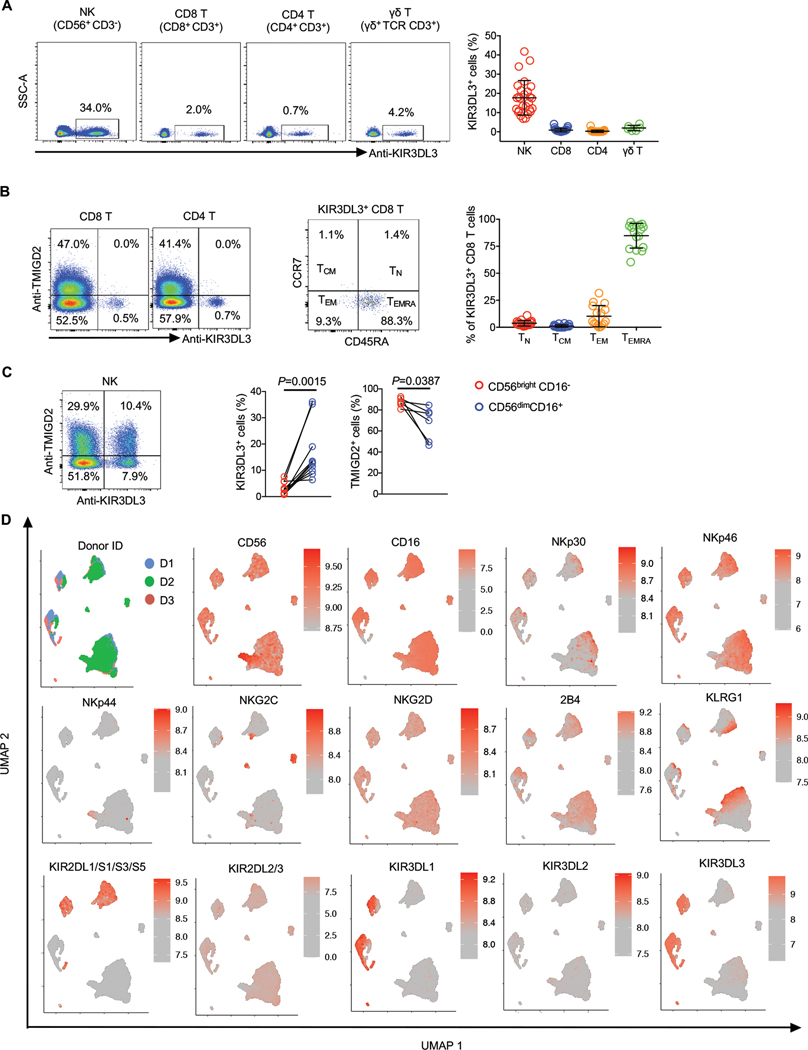
Fig. 2. KIR3DL3 was expressed on innate and adaptive immune cells.
(A) Flow cytometric analysis of KIR3DL3 expression on PBMCs. Left: KIR3DL3 expression on indicated subsets from one donor. Right: The frequencies of KIR3DL3+ cells in the indicated subsets (n=27 for NK, CD4 T, and CD8+ T; n=7 for γδ T). Data are represented as mean ± SD.
(B) Left: The expression pattern of KIR3DL3 and TMIGD2 on CD4 and CD8+ T cells. Middle: The distribution of KIR3DL3+ CD8+ T cells based on the coordinate expression of CD45RA and CCR7. Right: The summary of the distribution of KIR3DL3+ CD8+ T cells (n=16). Data are represented as mean ± SD.
(C) Left: The co-expression pattern of KIR3DL3 and TMIGD2 on NK cells. Right: The frequencies of KIR3DL3+ and TMIGD2+ cells in the indicated NK subsets (KIR3DL3: n=8; TMIGD2: n=6). P values by a two-tailed paired t-test.
(D) Human PBMCs were analyzed by spectral flow cytometry. The UMAP was generated based on flow cytometric data gated on NK cells (n=3).
In B (left) and C (left), data are representative of three independent experiments with different donors.