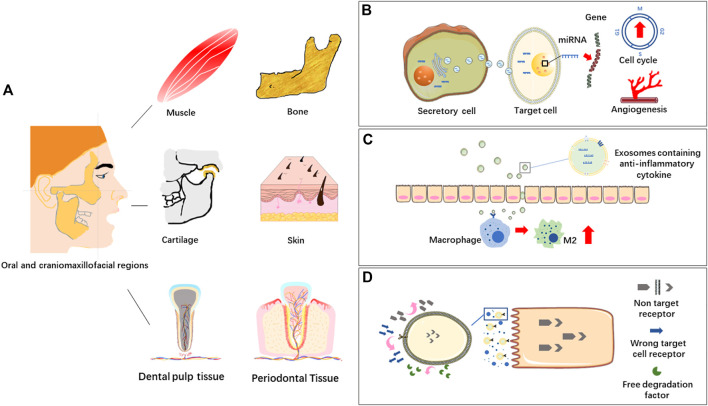
FIGURE 2.
(A) Oral and craniomaxillofacial tissues. (B) EVs in intercellular communication. Extracellular vesicles (EVs) transport bioactive molecules like miRNAs to regulate gene expression of target cells, affecting cell life activities, such as angiogenesis and cell cycle. (C) EVs in immunomodulation. EVs containing immunomodulating factors are transferred into macrophages to induce M2 polarization and thus inhibit inflammation. (D) EVs in targeted delivery system. EVs bind to target cells through the receptor-ligand system on the membranes.