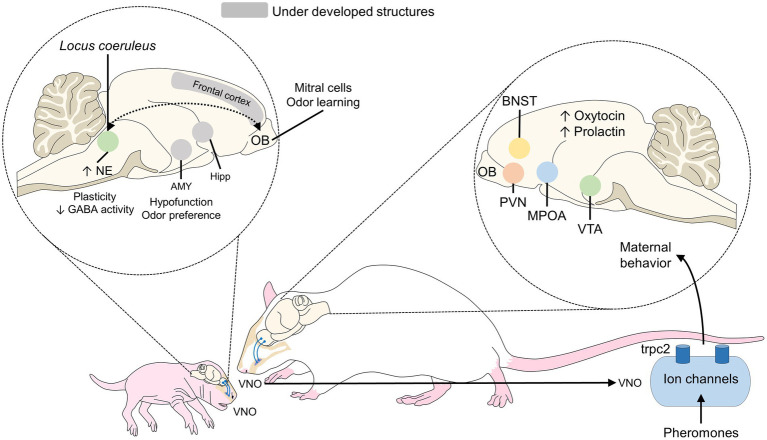
Figure 4.
Olfactory mother-young recognition in rodents. During this process in neonate rats, the hypofunction of the amygdala (to block odor preference) and the greater number of noradrenergic neurons in the locus coeruleus are the main features that promote the interaction. In mothers, oxytocin secretion and its action on the MPOA, VTA, PVN, and BNST are associated with the presentation of maternal behaviors. AMY, amygdala; BNST, bed nucleus of the stria terminalis; Hipp, hippocampus; GABA, gamma-aminobutyric acid; MPOA, medial preoptic area; NE, norepinephrine; OB, olfactory bulb; PVN, paraventricular nucleus; VTA, ventral tegmental area.