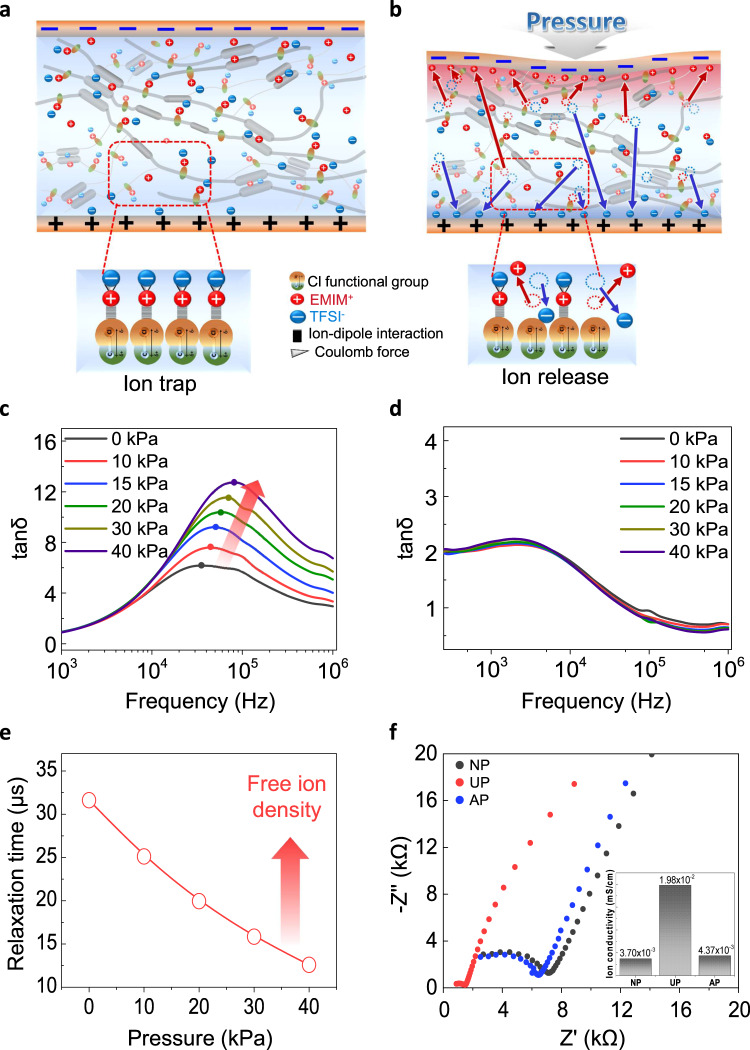
Fig. 4. Molecular design and working principle of the trap and release-based CLiPS device.
Design of the piezocapacitive device consisting of the CLiPS film sandwiched between AgNW/CLPU@E5 flexible electrodes (1 mV to 1 V). a Confinement of [EMIM]+[TFSI]- ion pairs to Cl groups (trapped state) at a pre-stimulus condition. b Schematic of CLiPS demonstrating the pumping of ions owing to pressure-impelled breaking of ion–dipole interactions under deformation and EDL formation at the CLiPS/electrode interface. Ion dynamics and free ion density of (c) CLiPS and (d) CLPU@E0-IL films with a stepwise pressure increase. CLiPS exhibits trap and release mechanism as the free ion density increases with pressure. e Charge relaxation time decreases with increased pressure input owing to the release of more free ions in the CLiPS. f Nyquist plot of CLiPS under no pressure (NP), under pressure (UP), and after removing pressure (AP), confirming reversible movement of ions (insert shows ion conductivity under each condition).