FIGURE 7.
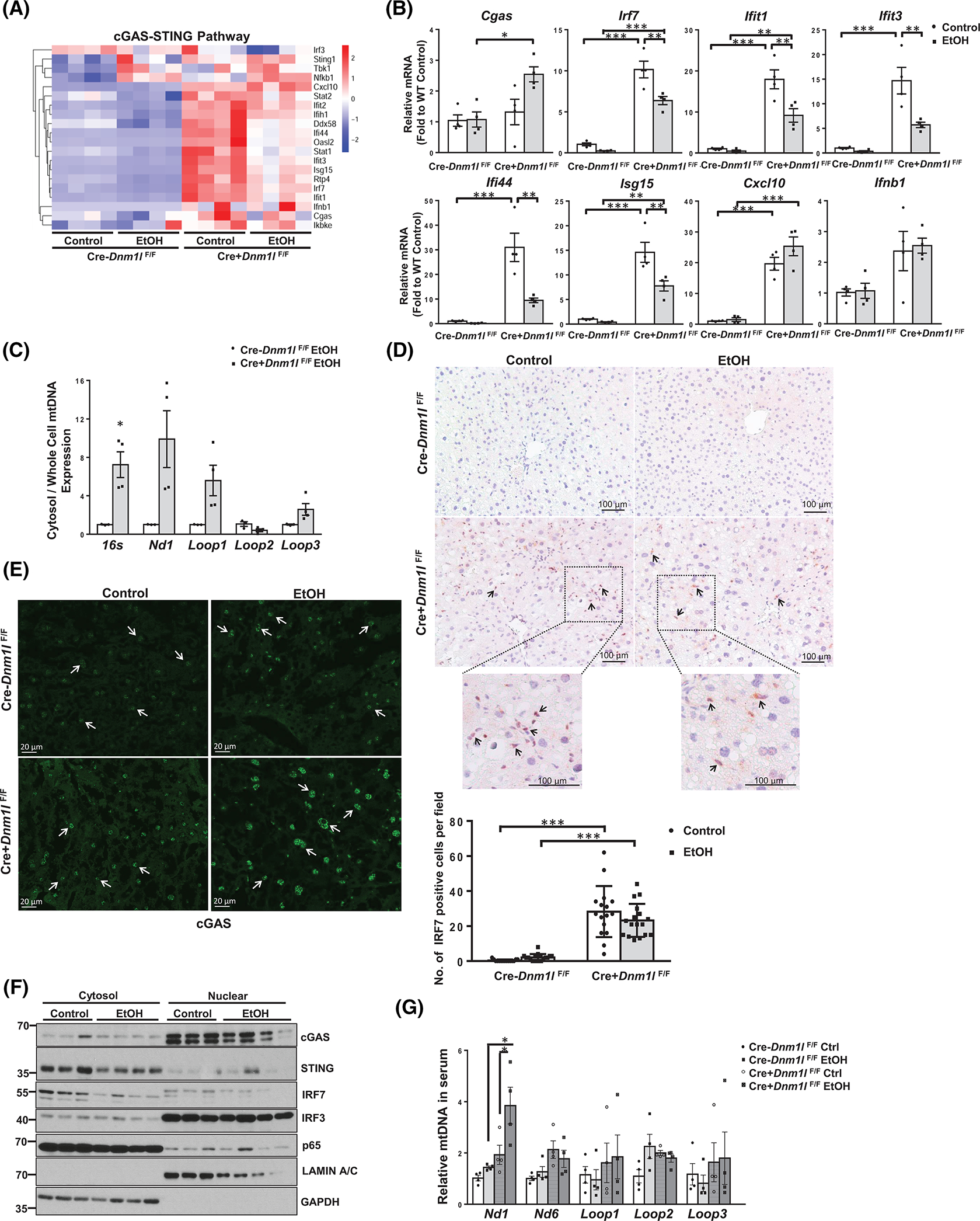
Loss of dynamin-related protein 1 (DRP1) promotes cyclic guanosine monophosphate–adenosine monophosphate synthase (cGAS)–stimulator of interferon genes (STING)–interferon regulatory factor (IRF)3/7 innate immune pathway in mouse liver. (A) Heatmap analysis of cGAS-STING pathway involved genes from the RNA-sequencing dataset of liver tissues of indicated mice fed with Gao-binge alcohol. (B) qPCR analysis of the cGAS-STING pathway genes in mouse liver. (C) DNA in the cytosol and whole cells was purified from isolated hepatocytes of liver-specific DRP1 knockout (L-DRP1 KO) and wild-type (WT) mice fed with Gao-binge alcohol. The relative abundance of mtDNA in the cytosol was quantified by qPCR using the whole-cell mtDNA content as an internal control. IHC staining for IRF7 (D) and immunofluorescence staining for cGAS in mouse livers (E). Arrows denote positive IRF7 stained nonparenchymal cells and nuclear cGAS in hepatocytes. The number of IRF7 positive cells were quantified (n = 3). (F) Liver cytosol and nuclear fractions were subjected to western blot analysis. (G) The relative abundance of mtDNA in serum was quantified by real-time polymerase chain reaction. Data are presented as means ± SEM in (B-C and G) (n = 3–4), means ± SD in (E). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001; one-way analysis of variance analysis with Bonferroni’s post hoc test. EtOH, ethanol; mRNA, messenger RNA; mtDNA, mitochondrial DNA; qPCR, real-time
