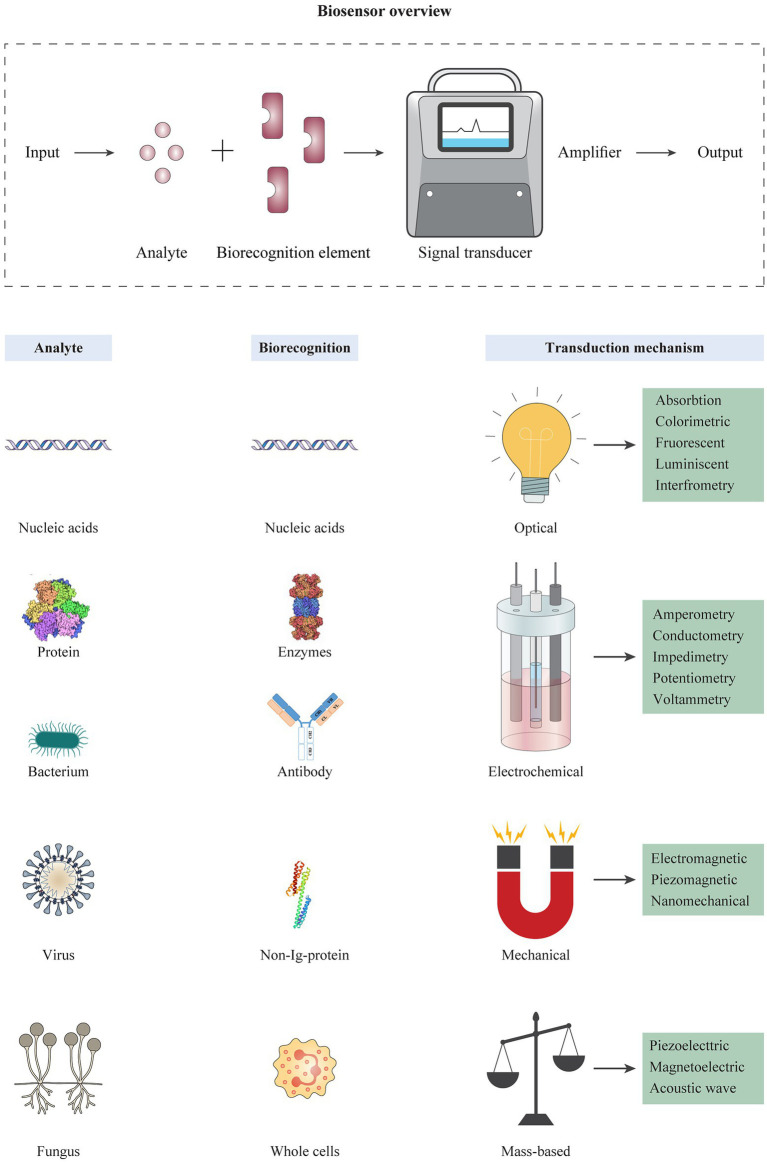
Figure 3.
Schematic overview of biosensor platforms consisting of different types of analytes, biorecognition elements, and transduction mechanisms. The operation of a biosensor is based on detection of an analyte by a highly specific biorecognition element. Analytes usually include biomolecules such as nucleic acids, proteins, and different cells. The reaction of an analyte with the biorecognition element is transformed into an electrical, optical, or electrochemical signal by a transducer, and converted into displayable data. The different types of biorecognition elements are used in the design of biosensors, including nucleic acids, antibodies, non-long-proteins, and/or synthetic ligands. Biosensors can be categorized based on the transducing mechanism, including optical, electrochemical, mechanical, and mass-based biosensors, which each category contains several platforms.