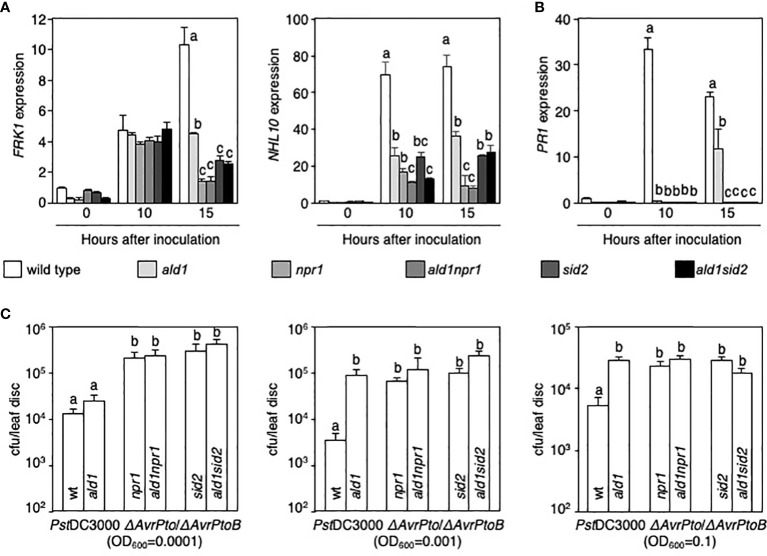
Figure 2.
Mutations of ALD1, NPR1, and ICS1/SID2 cause hypo-resistance against an attenuated strain of Pseudomonas syringae infection. (A, B) Relative expression levels of FRK1 and NHL10 (A) and PR1 (B) in leaves of WT and mutants infected with PstDC3000 ΔAvrPto/ΔAvrPtoB (OD600 = 0.01). The columns and bars show the average with standard deviation obtained from three biological replications (number of technical replicates = 3). (C) Growth of PstDC3000 ΔAvrPto/ΔAvrPtoB strain in WT and mutants. An attenuated strain was syringe-infiltrated into the leaves of WT, single, and double mutants (OD600 = 0.0001 or 0.001) (left and middle panels), or the strain was also applied to Arabidopsis plants with a spray (OD600 = 0.1) (right panel). The number of bacteria was counted on day 3 or 5 after inoculation. Error bars indicate standard error (n = 10 or 12). The experiment was repeated twice with the same results. Statistically significant differences are shown using different letters (p < 0.05 [A, B], p < 0.01 [C], one-way ANOVA).