Figure 1.
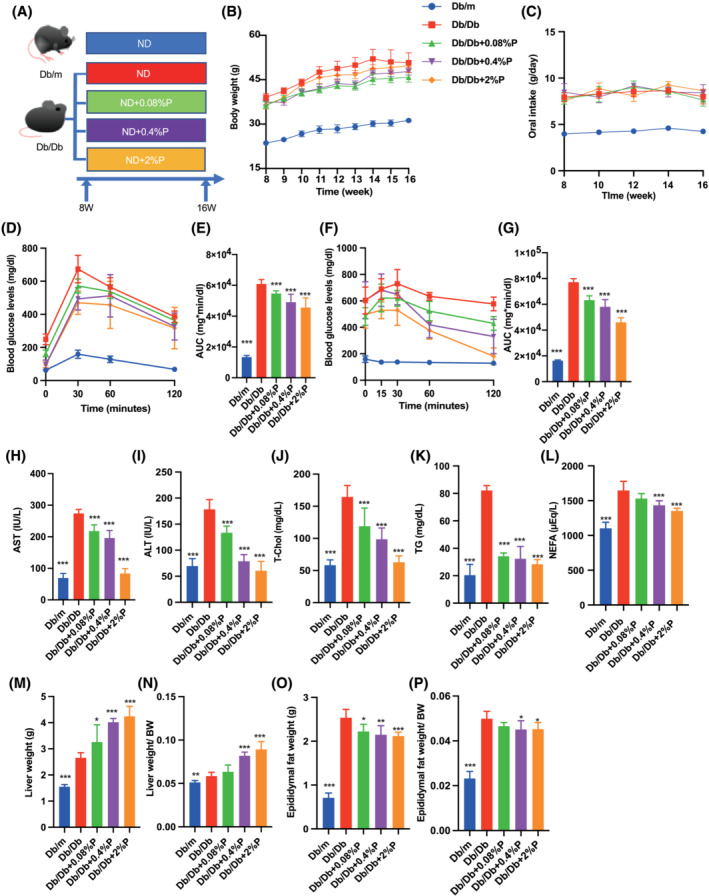
Administration of propolis improved obesity, glucose tolerance, hepatic enzymes, lipid metabolism and visceral fat obesity. (A) Administration of propolis (0.08, 0.4 and 2% per feed weight) started at 8 weeks of age. (B) Changes in the body weight (n = 12). (C) Oral intake (g/day) (n = 12). (D and E) Results of intraperitoneal glucose tolerance test (2 g/kg body weight) for 15‐week‐old mice and the area under the curve (AUC) analysis (n = 12). (F and G) Results of insulin tolerance test (0.75 U/kg body weight) for 15‐week‐old mice and the AUC analysis (n = 12). (H–L) Serum aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), total cholesterol (T‐Chol), triglyceride (TG) and non‐esterified fatty acid (NEFA) levels (n = 12). (M and N) Absolute and relative weights of liver (n = 12). (O and P) Absolute and relative weights of epididymal fat (n = 12). Data are represented as the mean ± SD values. Data were analysed using one‐way ANOVA with Holm–Šídák's multiple‐comparisons test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.
