Figure 4.
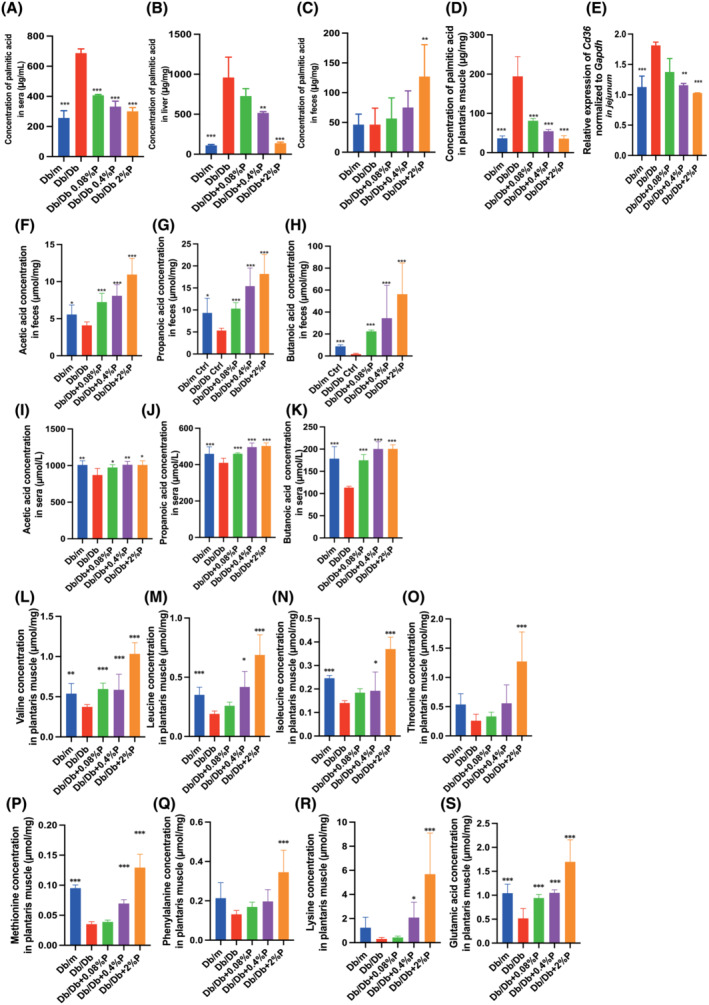
Administration of propolis decreased the Cd36 mRNA levels, which resulted in decreased concentration of saturated fatty acids in sera, liver and soleus muscle and increased concentration in faeces. The administration of propolis increased the concentration of short‐chain fatty acid in faeces and sera and the concentration of the amino acids related to muscle biosynthesis. The concentration of palmitic acid in (A) sera, (B) liver, (C) faeces and (D) soleus muscle (n = 12). (E) Relative mRNA expression of Cd36 in the jejunum normalized to the expression of GAPDH (n = 12). The concentrations of (F) acetic acid, (G) propanoic acid and (H) butanoic acid in faeces (n = 12). The concentrations of (I) acetic acid, (J) propanoic acid and (K) butanoic acid in sera (n = 12). The concentrations of (L) valine, (M) leucine, (N) isoleucine, (O) threonine, (P) methionine, (Q) phenylalanine, (R) lysine and (S) glutamic acid in the plantaris muscle (n = 12). Data are represented as the mean ± SD values. Data were analysed using one‐way ANOVA with Holm–Šídák's multiple‐comparisons test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.
