Figure 4.
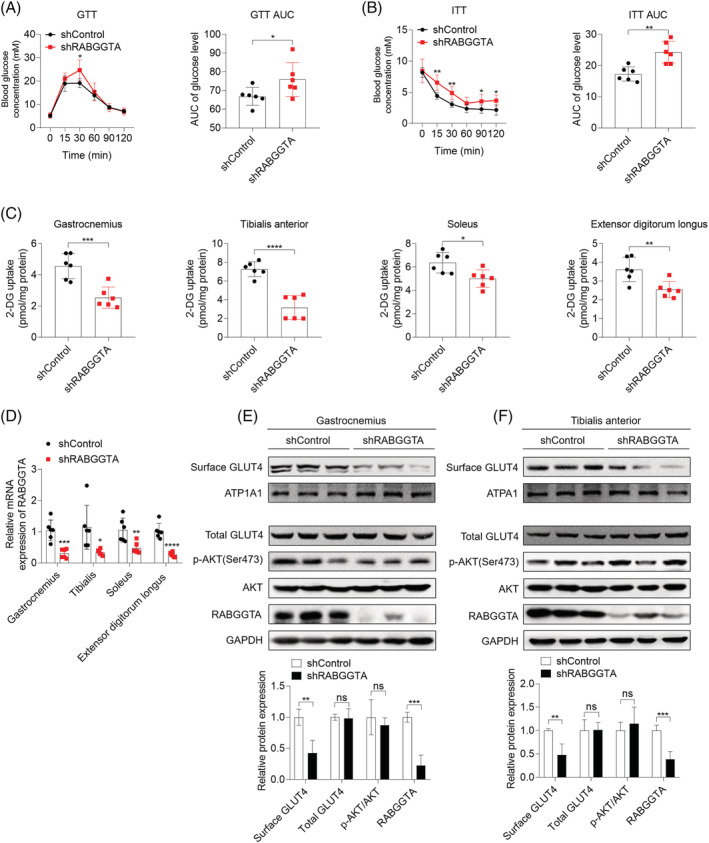
Adeno‐associated virus serotype 9 (AAV9)‐mediated knockdown of RABGGTA in skeletal muscle causes insulin resistance without disturbing insulin signalling in vivo. Mice were subjected a week of adjustable feeding and then were divided into two groups including shControl group and shRABGGTA group (n = 6). Posterior limbs of mice in shControl group and shRABGGTA group were infected with control AAV9 and shRABGGTA AAV9, respectively, through in situ injection. Four weeks after the infection, mice were subjected with experiments as follows. (A) Glucose tolerance test (GTT) and GTT AUC. (B) Insulin tolerance test (ITT) and ITT AUC. (C) Mice were fasted for 16 h before intraperitoneal injection of 2‐DG (2 g/kg body weight). Thirty minutes after the injection, mice were sacrificed and skeletal muscle including gastrocnemius, soleus, tibialis anterior, and extensor digitorum longus was obtained. 2‐DG concentration in each muscle was measured using Glucose Uptake Colorimetric Assay Kit. (D) The mRNA expression of RABGGTA in skeletal muscle was quantified by RT‐qPCR. (E, F) The expression of indicated proteins in gastrocnemius (E) and tibialis anterior (F) was detected by western blot, with GAPDH as the loading control of total protein and ATP1A1 as the loading control of plasma membrane protein (n = 3). Data represented the mean ± SEM. Statistical analysis was performed with one‐way ANOVA. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001; ns denotes no significance.
