Figure 18.
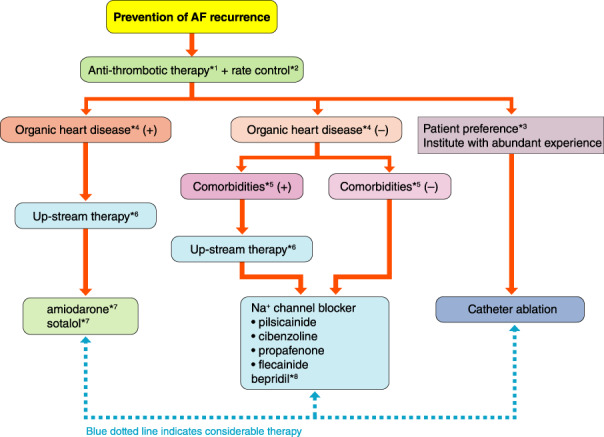
Flowchart for prevention of AF. *1Anticoagulation therapy might be continued depending on individual risks for embolism and efficacy of AF preventive therapy (see “Chapter V. 3 Anticoagulation Therapy” for details). *2Rate control therapy might be continued in cases of possible AF recurrence and considerable symptoms during AF (see “Chapter V. 4 Rate Control Therapy” for details). *3See the “Guidelines for Non‐Pharmacological Therapy”, 2018 edition 3 for details. *4Hypertrophic heart, heart failure, ischemic heart disease. *5Hypertension, dyslipidemia, diabetes, obesity, chronic kidney disease, sleep apnea syndrome, etc. (see “Chapter V. 2.5 Management of Risk Factors and Comorbidity” for details). *6Appropriate therapeutic intervention for basic and/or complicated diseases (see “Chapter V. 6 Upstream Therapy” for details). *7Insurance coverage for amiodarone is approved in Japan only for patients with AF and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy or heart failure. Insurance coverage for sotalol is not approved for patients with AF, although the efficacy of sotalol on AF complicated with ischemic heart disease. *8bepridil is reported to be effective for AF with ventricular dysfunction; however there are reports warning of exaggeration of proarrhythmia. AF, atrial fibrillation.
