FIGURE 2.
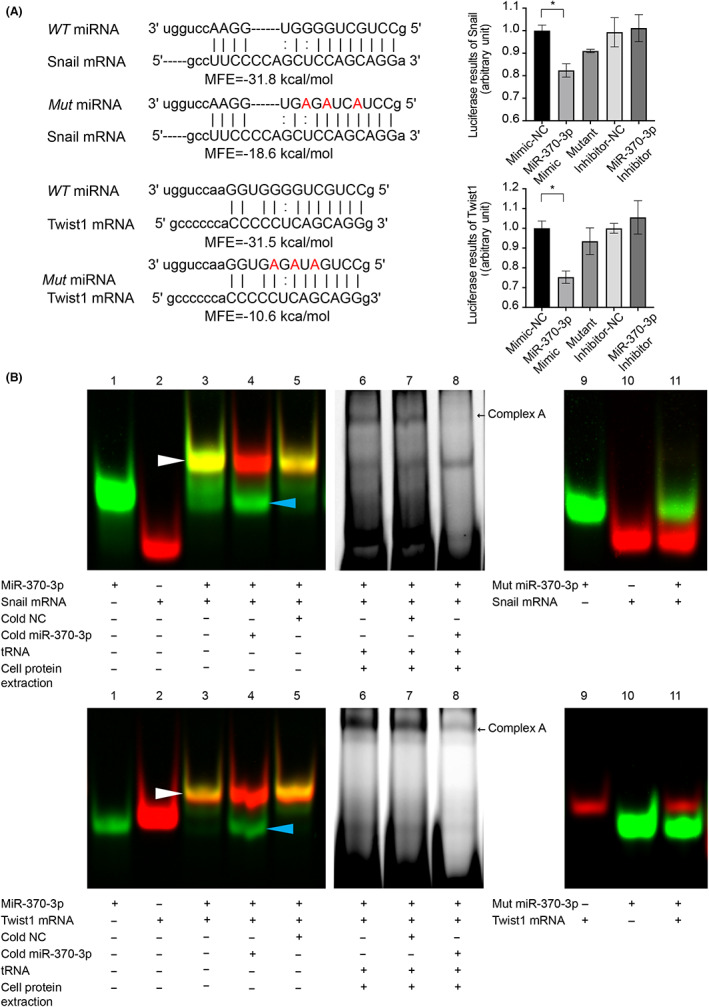
Identification of Snail and Twist1 as direct effectors of microRNA (miR)‐370‐3p. (A) Predicted hybrid complexes formed by miR‐370‐3p and sequences within the 3′‐UTR of WT Snail and Twist1 mRNA. The free energy of hybridization between miR‐370‐3p and Snail 3′‐UTR was −31.8 kcal/mol, and Twist1 3′‐UTR was −31.5 kcal/mol. When three nucleotides in miR‐370‐3p sequence were mutated, the free energy of hybridization was reduced to −18.6 and − 10.6 kcal/mol, respectively. (B) RNA EMSAs showed that miR‐370‐3p oligonucleotides interacted with Snail and Twist1 mRNA oligonucleotides directly. Lane 1, free miRNA; lane 2, free mRNA; lane 3, miRNA + mRNA; lane 4, miRNA + mRNA + cold hsa‐miR‐370‐3p; lane 5, miRNA + mRNA + cold negative control (NC, cold NC does not affect hybridization); lanes 6–8, RNA : protein interactions. After adding cell cytoplasmic extract to reaction mixtures, miRNA/mRNA/protein complex formation occurred (complex A). Complex A was competitively inhibited by 50‐fold molar excess of cold miR‐370‐3p (lane 8). Mutated miR‐370‐3p failed to form miRNA/mRNA hybridization (lanes 9–11). (C) Luciferase activity of the luciferase reporter constructs containing either WT or mutated 3′‐UTRs of Snail and Twist1 after miR‐370‐3p mimic treatment. *p < 0.05.
