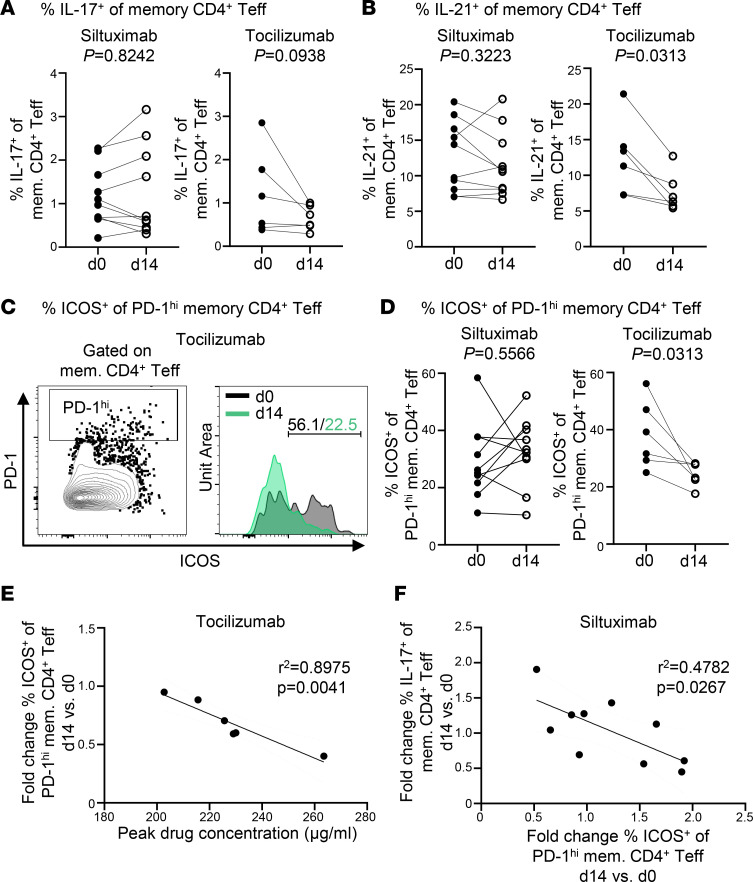
Figure 2. Tocilizumab but not siltuximab decreases ICOS expression of T follicular helper cells.
Thawed and rested PBMCs from siltuximab-treated or tocilizumab-treated patients with T1D were stimulated with PMA/ionomycin for 1 hour followed by an additional 3 hours in the presence of Brefeldin A. Each line represents an individual patient; n = 10 for siltuximab and n = 6 for tocilizumab. Solid circles represent d0 prior to drug infusion, and open circles represent d14 after drug infusion. (A) Frequency of IL-17+ cells in memory CD4+ Teffs. (B) Frequency of IL-21+ cells in memory CD4+ Teffs. (C) Representative histograms showing PD-1hi ICOS+ memory CD4+ Teffs at d0 and d14 after tocilizumab infusion from a single patient. (D) Frequency of ICOS+ cells in PD-1hi memory CD4+ Teffs. (E) Linear regression for tocilizumab cohort showing negative correlation between peak drug concentration on d1 and fold change d14 versus d0 for frequency of ICOS+ cells in PD-1hi memory CD4+ Teffs. (F) Linear regression for siltuximab cohort showing negative correlation between fold change d14 versus d0 for frequency of ICOS+ cells in PD-1hi memory CD4+ T cell compartment and fold change d14 versus d0 for frequency of IL-17+ cells in memory CD4+ T cell compartment. Statistical tests: (A, B, and D) Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed-rank test; and (E and F) linear regression.