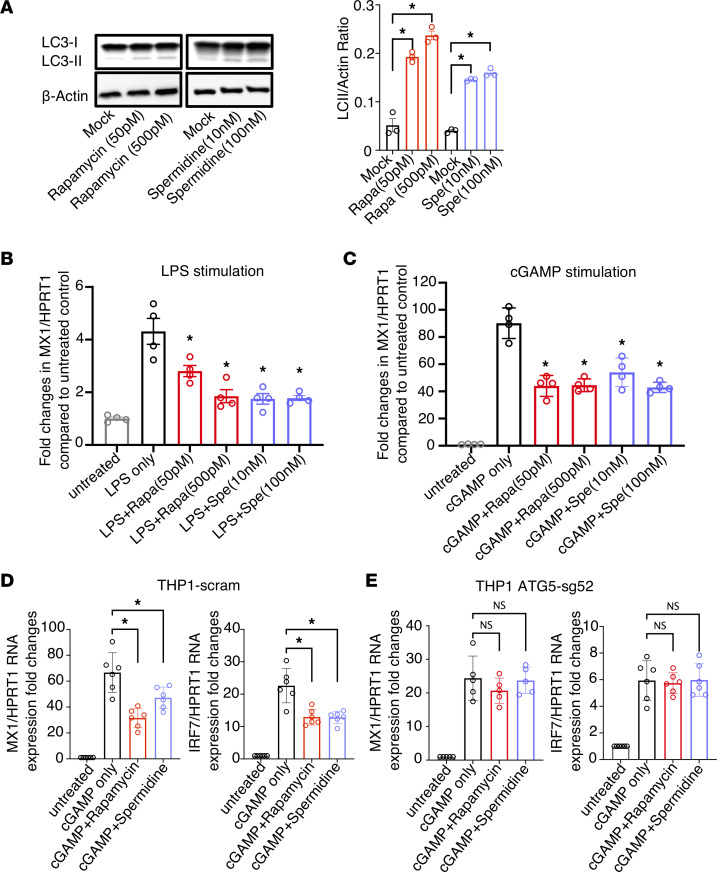
Figure 2. Autophagy induction by rapamycin (Rapa) reduces IFN-I signaling in activated macrophages and THP1 cells and is dependent on ATG5.
CD14+ monocytes were sorted from healthy primary PBMCs with CD14 microbeads and differentiated into macrophages with macrophage colony-stimulating factor at 10 ng/mL for 3 days. Afterward, cells were treated with the autophagy inducers rapamycin (50 pM and 500 pM) or spermidine (Spe; 10 nM and 100 nM) for 2 days. (A) Autophagy flux was measured by western blotting for LC3 and actin. The ratio of LC3-II/actin was calculated by ImageJ. After rapamycin or spermidine treatment, cells were stimulated by (B) LPS or (C) cGAMP for 6 hours; the ISG MX1 and internal control HPRT1 were measured by real-time PCR. (D and E) THP-1 scram (D) or THP-1 ATG5-sg52 (E) cells were treated with 50 pM rapamycin or 100 nM spermidine for 2 days and followed by cGAMP stimulation for 6 hours. The ISGs MX1 and IRF7 and the internal control HPRT1 were measured by real-time PCR. Data are reported as the mean values of 3–5 independent experiments ± SEM. *P < 0.05, Kruskal-Wallis analysis with Dunn’s test.