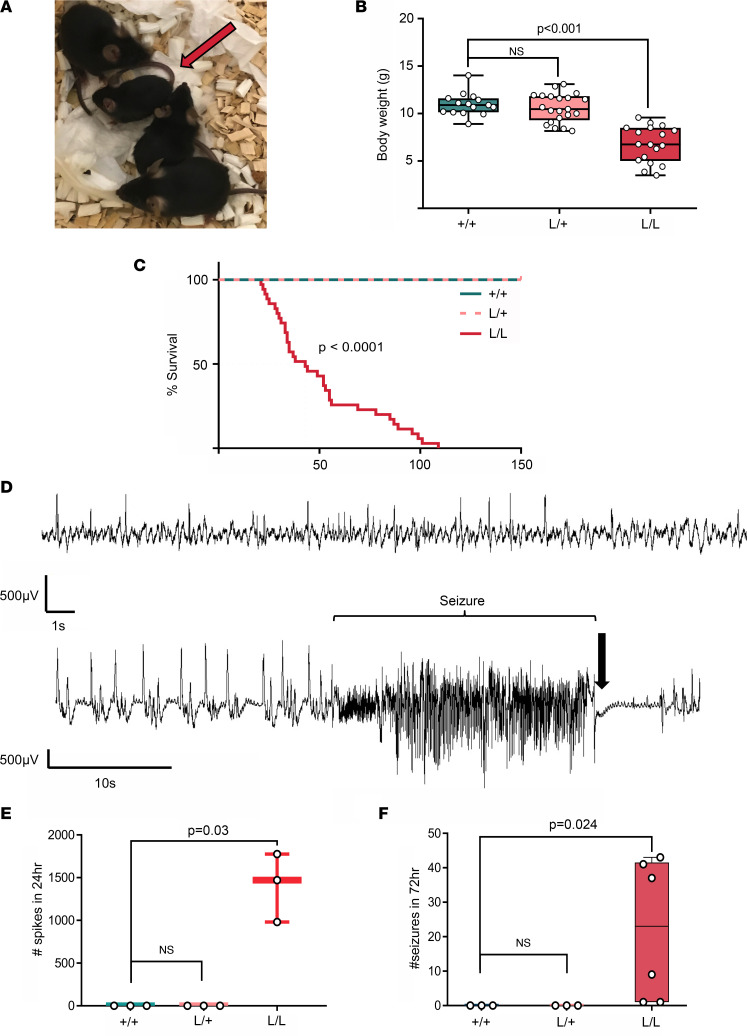
Figure 1. Phenotype of the Kcnt1 L/L mouse model.
(A) Difference in size at P21 of L/L mice (red arrow) compared with their L/+ and +/+ littermates. (B) Body weight is significantly reduced in L/L mice compared with their +/+ littermates at weaning age (Kruskal-Wallis test, followed by Dunn’s post hoc analysis; +/+ n = 15, L/+ n = 21, L/L n = 18). Data are presented in a box-and-whisker plot with maximal and minimal data points (whiskers) and median (line). (C) Life span is shortened in L/L mice with a median survival of 43 days (Kaplan-Meier curve, log-rank test P < 0.0001; +/+ n = 15, L/+ n = 15, and L/L n = 35). (D) Representative ECoG trace of ictal activity and interictal spikes in the L/L mice. Top: Acute interictal spikes. Bottom: Seizures can be preceded by an increase in frequency of acute interictal spikes. Spontaneous tonic-clonic seizures correlated with fast, high-amplitude signal, followed by electric suppression (black arrow). (E) Acute high-amplitude (>500 μV) spikes are present in the L/L mice, with a median of 1,470 spikes in 24 hours (P = 0.03, Kruskal-Wallis test, followed by Dunn’s post hoc analysis, n = 3 for each genotype). (F) Seizure frequency over 72 hours (+/+ n = 3, L/+ n = 3, L/L n = 6; median seizure frequency for L/L of 23 events. Kruskal-Wallis test, followed by Dunn’s post hoc analysis P = 0.024).