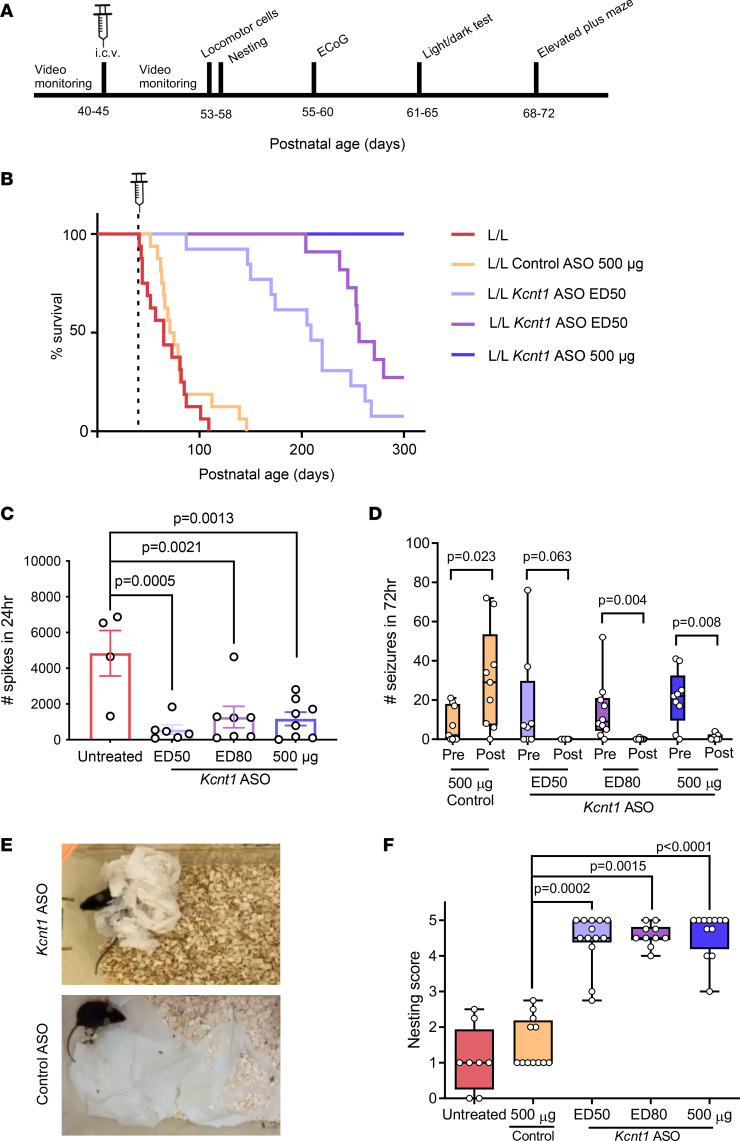
Figure 4. ASO-mediated knockdown of Kcnt1 at P40 markedly improves the disease phenotype of adult L/L mice.
(A) Experimental timeline for behavioral studies. (B) Kaplan-Meier curves show a dose-dependent improvement in survival of adult L/L mice treated with Kcnt1 ASO (P < 0.0001 for Kcnt1 ASO ED50, ED80, and 500 μg, log-rank test), while mice treated with control ASO showed a survival similar to that of untreated animals (P = 0.237, log-rank test, untreated n = 16, control ASO n = 16, Kcnt1 ASO ED50 n = 13, ED80 n = 11, 500 μg n = 11). (C) Acute spike frequency over 24 hours (untreated n = 4, Kcnt1 ASO ED50 n = 6, ED80 n = 7, 500 μg n = 8; 1-way ANOVA F[3, 21] = 7.978, P = 0.001). (D) Seizure frequency was significantly reduced after treatment with Kcnt1 ASO ED80 and 500 μg. Although ED50 did not reach statistical significance, a trend toward reduction was observed. Treatment with control ASO did not reduce the occurrence of seizures (control ASO n = 9; ED50 n = 8; ED80 n = 10, 500 μg n = 9; seizure frequency was compared using the nonparametric Wilcoxon matched pairs signed-rank test, with Pratt’s method for identical rows). (E) Representative images of nesting behavior of Kcnt1 ASO ED80 (top) and control ASO–treated (bottom) L/L mice. (F) Nesting score of animals treated with Kcnt1 ASO showed a significant improvement compared with control ASO–treated animals (ED50 vs. control P = 0.0002; ED80 vs. control P = 0.0015; 500 μg vs. control P < 0.0001; untreated vs. control P > 0.9. Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s post hoc analysis. Untreated n = 8, control ASO n = 12; ED50 n = 13; ED80 n = 10, 500 μg n = 12). Data are presented in a box-and-whisker plot with maximal and minimal data points (whiskers) and median (line).