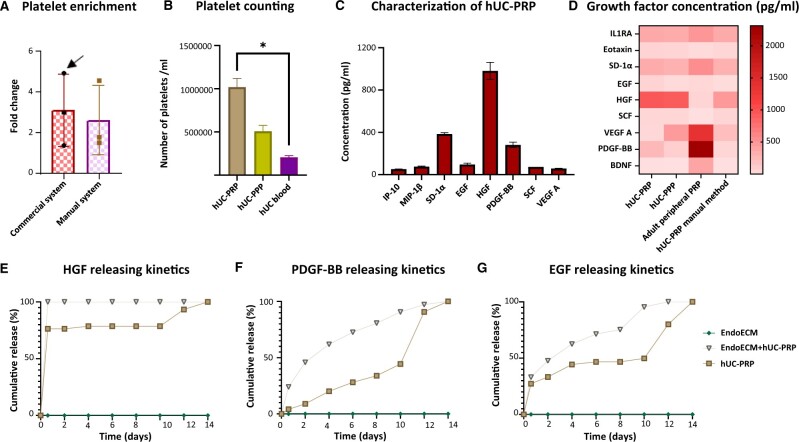
Figure 2.
hUC-PRP characterization, composition and in vitro releasing kinetics. (A) Comparison of platelet enrichment using commercial and manual methods for PRP extraction. Platelet enrichment was defined as the number of platelets in the hUC-PRP, divided by the number of platelets in whole hUC blood. The most enriched sample (indicated with an arrow) was selected for subsequent analyses. (B) Comparison of platelet density in hUC-PRP, hUC-PPP and whole hUC blood. (C) Predominant results from the multiplex protein assay for cytokines, chemokines and growth factors in hUC-PRP. (D) Comparative heat-map of protein differences found among hUC-PRP and hUC-PPP extracted with a commercialized system, PRP from adult peripheral blood and hUC-PRP extracted with double centrifugation. (E–G) Releasing kinetics of (E) HGF, (F) PDGF-BB and (G) EGF in EndoECM + hUC-PRP, EndoECM and hUC-PRP conditions. The cumulative release was defined as the cumulative concentration released at each point, with respect to the total concentration released on day 14. Data in A–D are presented as a mean of three replicates ± SD. *P < 0.05. EGF, epidermal growth factor; EndoECM, decellularized porcine endometrium-derived extracellular-matrix hydrogel; HGF, hepatic growth factor; hUC, human umbilical cord; hUC-PRP, platelet-rich plasma from hUC; hUC-PPP, platelet-poor plasma from hUC; IP10, C-X-C motif chemokine 10; MIP-1β, C-C motif chemokine 4; PDGF-BB, platelet-derived growth factor-BB; SCF, stem cell factor; SDF1α, stromal cell-derived factor 1 A; VEGF A, vascular endothelial growth factor.