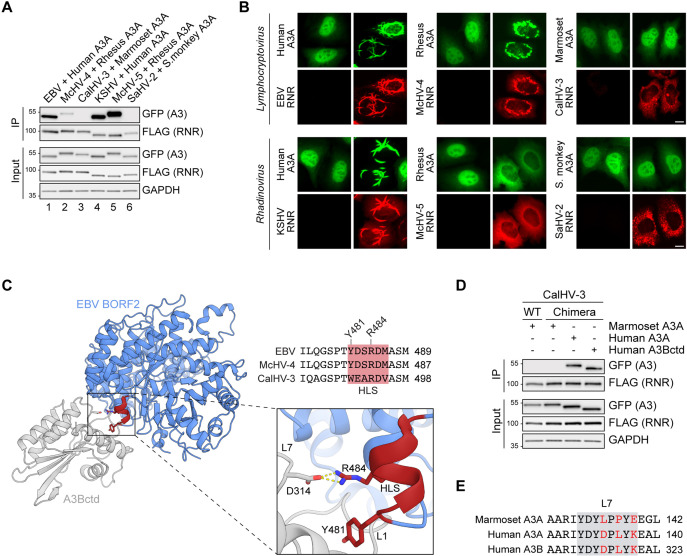
Figure 7. A short helical loop structure from Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) BORF2 enables the marmoset CalHV-3 ribonucleotide reductase (RNR) to bind to human A3B and A3A.
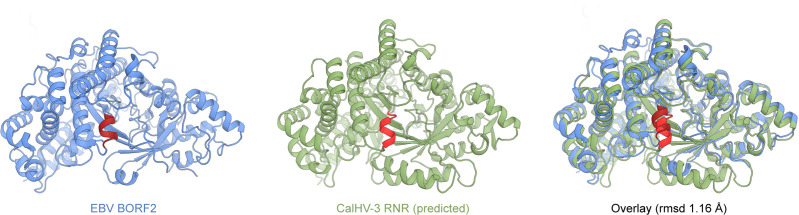
(A) Co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) of human, rhesus macaque, marmoset, and squirrel monkey A3As with the indicated gamma-herpesvirus RNR subunits. FLAG-tagged RNR subunits were co-expressed with the indicated A3-EGFP constructs in 293T cells, affinity purified, and analyzed by immunoblotting to detect co-purifying A3 proteins. (B) Representative IF microscopy images of HeLa cells co-transfected with the indicated FLAG-tagged viral RNRs (red) and A3A-EGFP constructs (green). Scale = 10 μm. (C) Ribbon schematic of the EBV BORF2-A3Bctd complex (pdb 7rw6, chains A and B) with BORF2 in blue and A3Bctd in gray. The helical loop structure (HLS) of EBV BORF2 is depicted in red. Bottom-right: zoom-in of the interacting surfaces highlighting BORF2 Y481 and R484 interactions with A3B loops 1 and 7, respectively. Top-right: amino acid alignment of the HLS regions of the EBV, McHV-4, and CalHV-3 RNRs (red boxes) and adjacent residues. (D) Co-IP of marmoset A3A, human A3A, and human A3Bctd with wild-type (WT) or chimeric CalHV-3 RNR containing the HLS region of EBV BORF2. FLAG-tagged RNR subunits were co-expressed with the indicated A3-EGFP constructs in 293T cells, affinity purified, and analyzed by immunoblotting to detect co-purifying A3 proteins. (E) Amino acid alignment of the loop 7 regions of marmoset A3A, human A3A, and human A3B (gray boxes) with non-identical loop 7 residues highlighted in red.