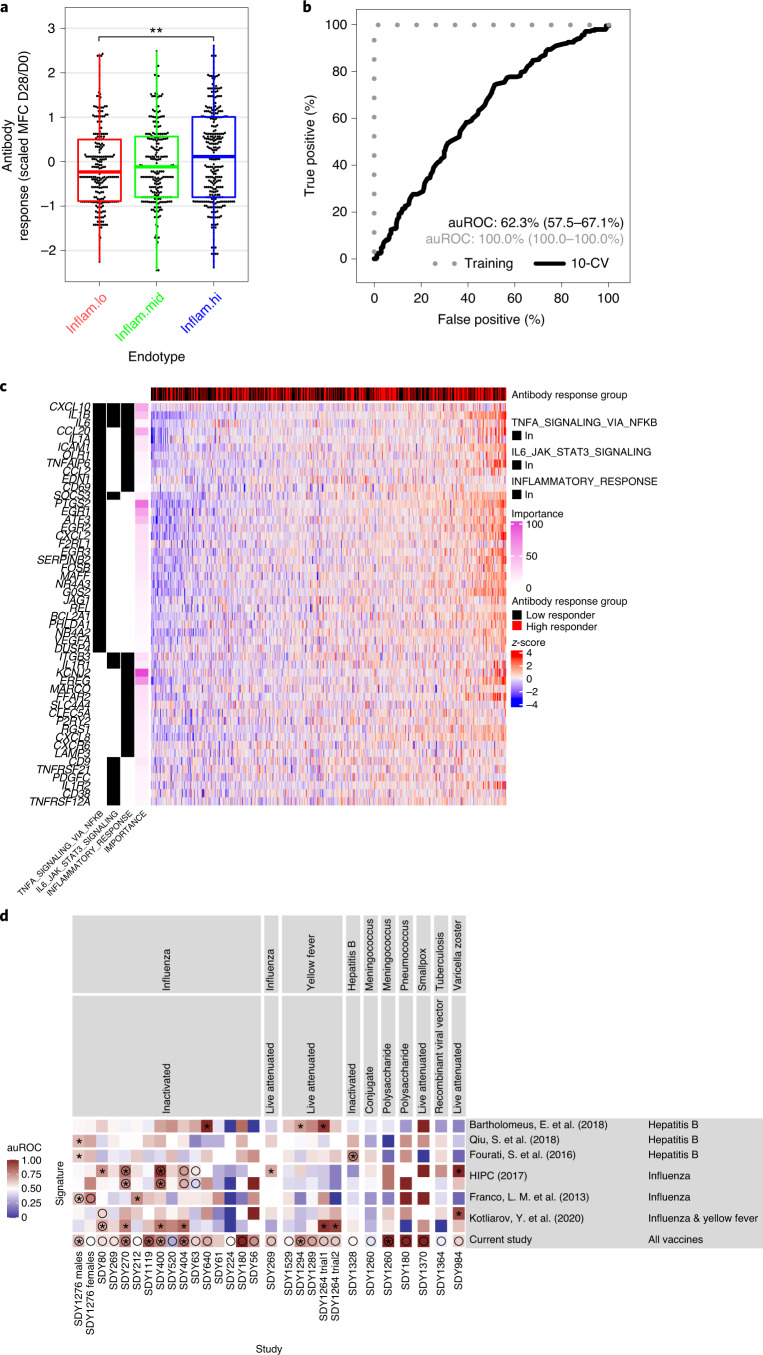
Fig. 4. Prediction of the antibody response by the pre-vaccination endotypes.
a, Box plot of the maximum fold change (MFC) antibody responses as a function of the pre-vaccination inflammation endotypes (inflam.lo, n = 212; inflam.mid, n = 233; inflam.hi, n = 281). The MFC was scaled to a mean of 0 and a standard-deviation of 1 across vaccines. For each boxplot, the vertical line indicates the median, the box indicates the interquartile range, and the whiskers indicate 1.5 times the interquartile range. A Wilcoxon rank-sum test without correction for multiple testing was used to assess differences in antibody response between the two endotypes; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001. b, A supervised machine-learning approach was adopted to train a random forest classifier using pre-vaccination gene expression to distinguish high vaccine responders (top 70%) from low vaccine responders (bottom 30%). The predictive performance of the classifier was assessed by tenfold cross-validation (10-CV). The ROC curve is presented along with the auROC and 95% confidence intervals estimated from the tenfold CV. c, The top 500 predictive genes/features included in the classifier (importance > 0%) overlapped with inflammatory genes identified in the unsupervised approach (two-sided Fisher’s exact test, P = 1.13 × 10−11). Heat map showing the pre-vaccination expression of the overlapping genes. Samples (columns) are ordered by increasing expression level of the inflammatory genes. A Wilcoxon rank-sum test was used to assess the association between the inflammatory signatures and high/low antibody response and resulted in a P value of 0.00265. d, Comparison of eight genes contributing the majority of the classifier prediction (importance > 50%) against previously identified pre-vaccination signatures of vaccine response. MetaIntegrator was used to calculate an auROC for each previously published pre-vaccination signature of vaccine response, as well as the eight genes identified in this work, using each of the transcriptomic studies within the Immune Signatures Data Resource. Circles correspond to studies that were used to train the pre-vaccination signatures, while asterisks indicate significantly better than random identification of high responders in each transcriptomic study as determined by a permutation test.