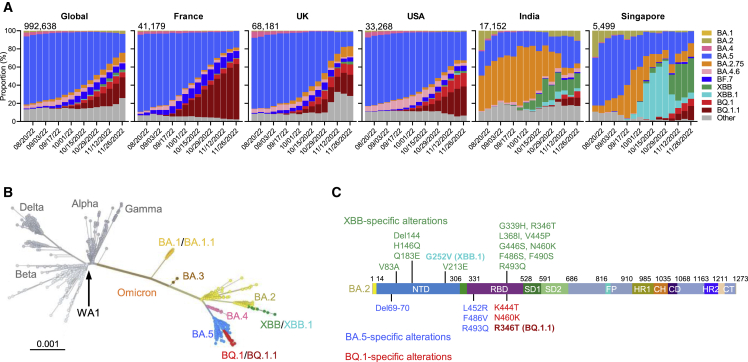
Figure 1.
The rise of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BQ.1, BQ.1.1, XBB, and XBB.1 subvariants
(A) Frequencies of Omicron subvariants from the Global Initiative on Sharing All Influenza Data (GISAID). Variants were designated according to their Pango dynamic lineage classification.12 Minor sublineages of each subvariant were grouped together with their parental variant. The values in the upper left corner of each box denote the cumulative number of sequences for all circulating viruses in the denoted time period.
(B) Unrooted phylogenetic tree of Omicron subvariants along with other main SARS-CoV-2 variants. The scale bar indicates the genetic distance.
(C) Key spike mutations found in XBB and XBB.1 in the background of BA.2 and in BQ.1 and BQ.1.1 in the background of BA.4/5. Del, deletion. The positions of these mutations on the spike trimer are shown in Figure S1.