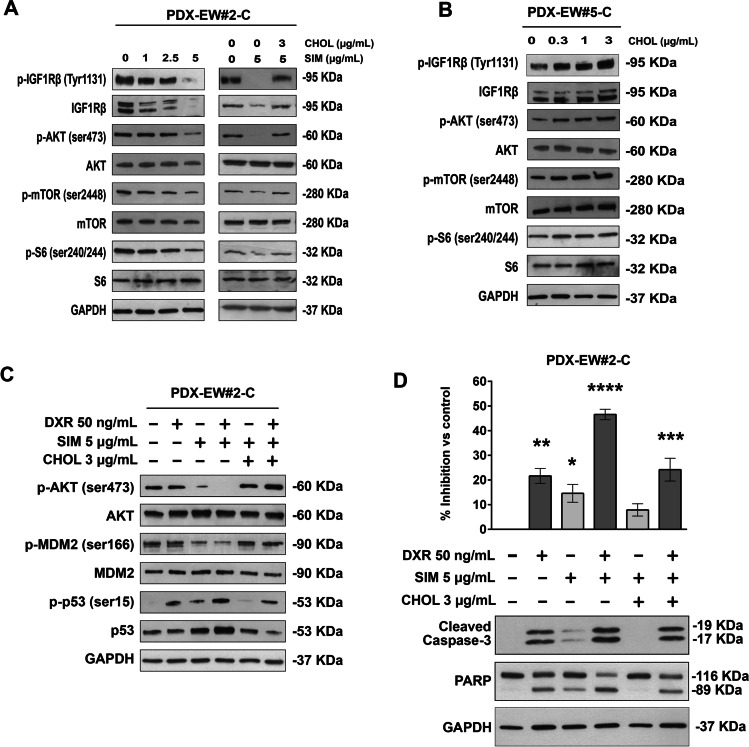
Fig. 6.
Cholesterol mediates activation of IGF1R/AKT signaling and doxorubicin-induced apoptosis. a, IGF1R pathway inhibition in PDX-EW#2-C (ABCA6low) cells treated with increasing doses of simvastatin (SIM) and after the rescue effect of exogenous cholesterol (CHOL) exposure. A representative western blot of three is shown. GAPDH was used as a loading control. b, IGF1R pathway induction in PDX-EW#5-C (ABCA6high) cells after exogenous cholesterol exposure. A representative western blot of three is shown. GAPDH was used as a loading control. c, AKT/MDM2/p53 proapoptotic pathway activation in PDX-EW#2-C cells after doxorubicin (DXR, 3 h) exposure alone or in combination with SIM or SIM plus CHOL. A representative western blot of three is shown. GAPDH was used as a loading control. d, Growth inhibition and apoptosis induction represented by caspase 3 and PARP cleavage, after doxorubicin (DXR, 24 h) exposure alone or in combination with SIM or SIM plus CHOL. Data in the graph are the mean ± SEM (n = 3); *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001. One–way ANOVA versus control (nontreated cells). A representative western blot of three is shown. GAPDH was used as a loading control