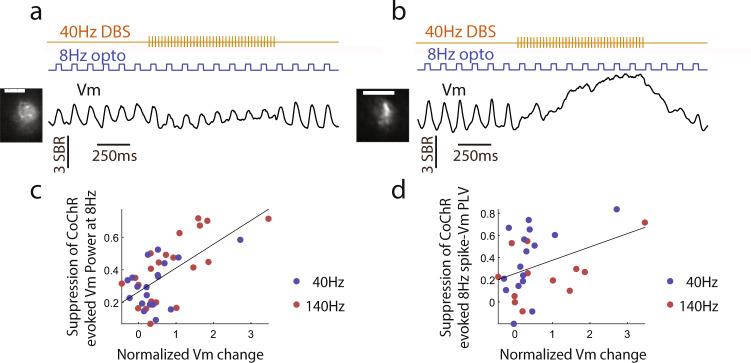
Fig. 8. DBS-induced membrane depolarization predicts suppression of optogenetic inputs.
a A single neuron example showing the trial-averaged Vm during 8 Hz CoChR activation and 40 Hz DBS. The Vm has been smoothed with a 30 ms rectangular window to better highlight the depolarization effect in response to 8 Hz CoChR activation. This neuron exhibited prominent optogenetics-evoked Vm depolarization without DBS, and reduced Vm depolarization during 40 Hz DBS. Average SomArchon fluorescence of the example neuron is shown in the left image. Scale bar, 15 µm (b) Same as (a), but another neuron example with strong Vm depolarization during 40 Hz DBS. c The reduction of optogenetically induced 8 Hz Vm power is shown as a function of Vm change (DBS – Baseline) during 40 Hz (blue dots) and 140 Hz (red dots) DBS. Vm change is normalized by the average spike amplitude for each recorded neuron. Each dot represents a neuron (n = 41 neurons total). Neurons with stronger DBS-evoked Vm depolarization exhibit greater suppression of the 8 Hz optogenetically induced Vm power. The black line represents the fitted linear regression line. d The reduction of optogenetically induced 8 Hz spike-Vm phase locking value (PLV) is shown as a function of Vm depolarization amplitude during 40 Hz (blue dots) and 140 Hz (red dots) DBS (n = 28 total neurons). Neurons with less than 5 spikes during stimulation and baseline were excluded from this analysis. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.