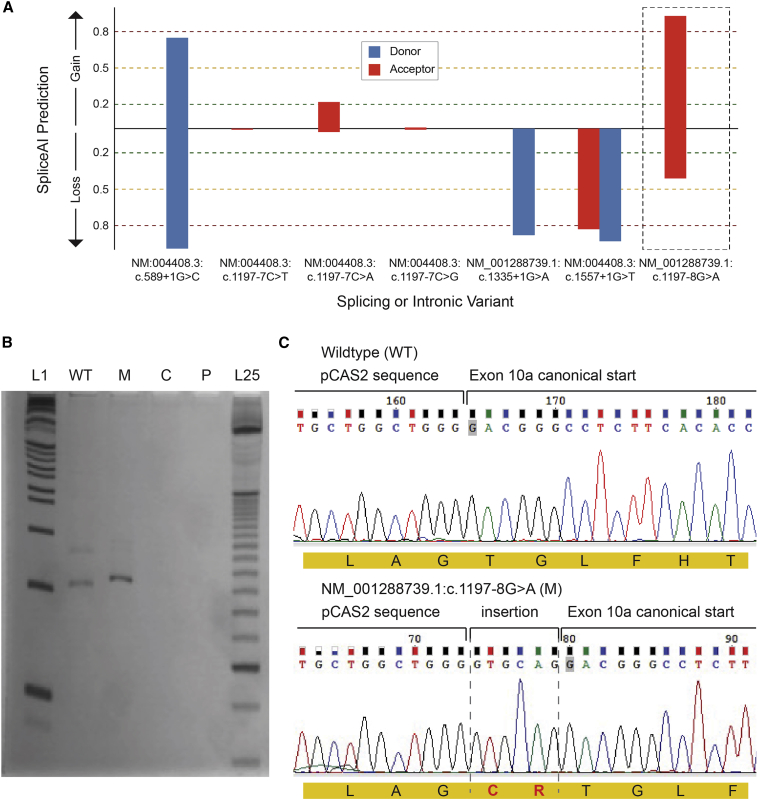
Figure 3.
Splicing assay assessing consequence of c.1197−8G>A (GenBank: NM_001288739.1) variant
(A) SpliceAI predictions for the consequence of population variants in gnomAD including curated, predicted loss-of-function splicing variants; variants at a position similar to the recurrent disease variant, i.e., c.1197−7 (GenBank: NM:004408.3); and the recurrent disease variant itself. Only the disease variant (c.1197−8G>A [GenBank: NM_001288739]) is strongly predicted to have an effect that may not be loss of function.
(B) cDNAs PCR products. L1, 1 Kb plus DNA ladder (Invitrogen); WT, wild-type amplification; M, mutant amplification; C, amplification from HEK293 cells without minigene transfection; P, PCR control without cDNA; L25, 25 bp ladder (Invitrogen).
(C) Sanger sequencing of wild-type and mutant PCR products. In red, the insertion of “GTGCAG” from 5ʹ of intron 9 to the mutant transcript, which results in a mutant protein with a cysteine and an arginine (CR) in-frame insertion after Arg399 residue.