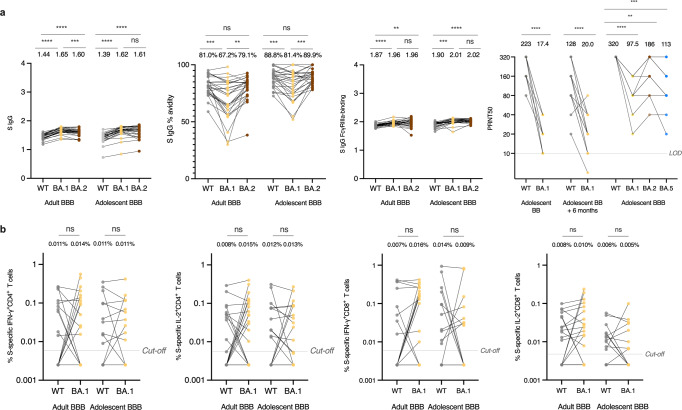
Fig. 3.
Humoral and cellular immunity is maintained against WT, Omicron BA.1 or BA.2, or BA.5 after the third dose of the BNT162b2 (BBB) vaccine in healthy evaluable adolescents and adults. a WT, BA.1, BA.2 and BA.5 SARS-CoV-2 Spike (S) IgG (Adult BBB N = 28, Adolescent BBB N = 28), S IgG avidity (Adult BBB N = 28, Adolescent BBB N = 28) and S IgG FcγRIIIa-binding (Adult BBB N = 28, Adolescent BBB N = 28) and PRNT50 (Adolescent BB N = 25, Adolescent BB + 6 months N = 25, Adolescent BBB N = 14) in evaluable adolescents and adults. Although antibody levels were quantitatively higher for BA.1 or BA.2 than WT, neutralisation was lower for BA.1, BA.2 or BA.5 than WT. b Omicron S WT reference pool and BA.1 mutation pool-specific interferon-γ (IFN-γ)+ CD4+ (Adult BBB N = 28, Adolescent BBB N = 22), interleukin-2 (IL-2)+ CD4+ (Adult BBB N = 28, Adolescent BBB N = 22), IFN-γ+ CD8+ (Adult BBB N = 28, Adolescent BBB N = 22), and IL-2+ CD8+ (Adult BBB N = 28, Adolescent BBB N = 22) T cells in evaluable adolescents and adults. The cellular responses were similar between WT and BA.1. Data labels and centre lines show geometric means (GM) estimates, with corresponding 95% confidence intervals shown by error bars. Dots representing the same participants are linked by a straight line. Statistical analysis was determined using paired t-test after natural logarithmic transformation with p values denoted. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001. ns not significant. LOD limit of detection, WT wild-type, FcγRIIIa Fcγ receptor IIIa, PRNT plaque reduction neutralisation test. Cut-offs were drawn as grey lines