Figure 2. Conservation of human fetal RLsvz gene signatures in Group 3/4-MB.
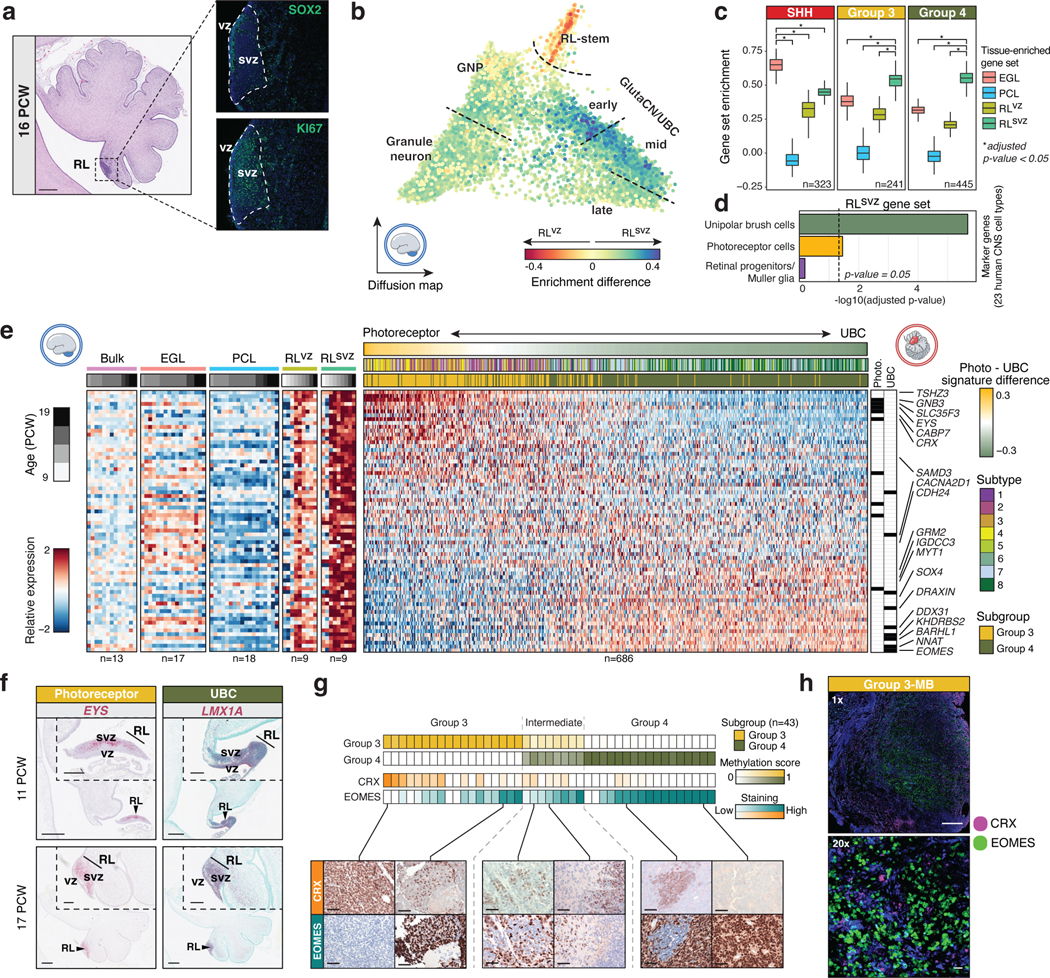
(a) (Left panel) H&E staining of the early (16 PCW) human cerebellum highlighting the densely populated RL. Scale bar, 500μm. (Right panels) SOX2 and KI67 immunostaining illustrate compartmentalization of the human fetal RL. (b) Enrichment of bulk RLvz and RLsvz expression signatures in human cerebellar glutamatergic lineages. (c) Enrichment of cerebellar compartment-specific gene sets by MB subgroup. P-values were calculated using the two-sided Mann–Whitney U-test and were adjusted for multiple comparisons using FDR correction. Boxes represent the median, first and third quartiles, with whiskers extending to 1.5x the interquartile range. (d) Enrichment of the RLsvz gene set in human CNS cell types. P-values were calculated using a one-sided Fisher’s exact test. (e) Expression heatmap of RLsvz marker genes in micro-dissected human cerebellar and Group 3/4-MB samples. (f) ISH of RLsvz-derived photoreceptor (EYS) and UBC (LMX1A) gene set markers in the fetal human cerebellum. Scale bars, 500μm and 200μm (inset). (g) IHC of CRX and EOMES in a series of Group 3/4-MB tumors (n=43). Scale bars, 40μm. (h) Dual immunofluorescence imaging of CRX and EOMES expression in a Group 3-MB. Scale bars, 1mm (upper panel) and 20μm (lower panel).
