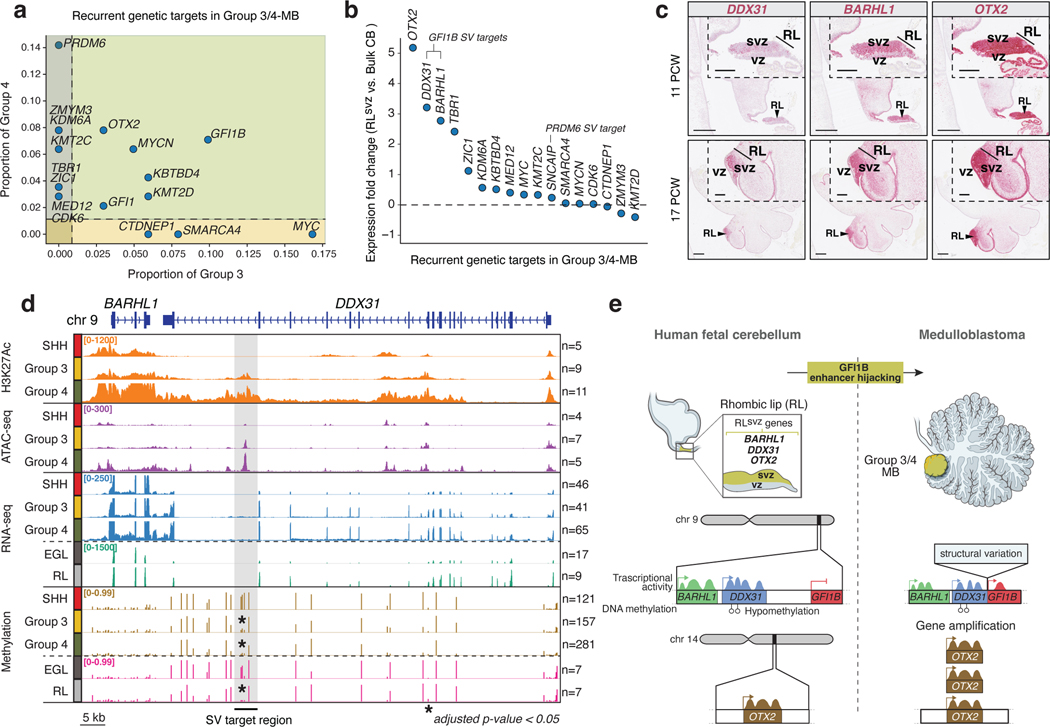
Figure 3. Genetic targeting of RLsvz markers in Group 3/4-MB.
(a) Incidence and distribution of MB-associated driver gene alterations in Group 3/4-MB. (b) Expression fold-change of Group 3/4-MB genetic targets in human fetal RLsvz versus bulk cerebellum. (c) ISH confirmation of spatially restricted DDX31, BARHL1, and OTX2 expression in the RL. Scale bars, 500μm and 200μm (inset). (d) Chromatin, transcriptional, and DNA methylation signatures at the BARHL1/DDX31 locus in MB and fetal human cerebellum. Shaded region indicates the minimal SV target region associated with GFI1B enhancer hijacking. Asterisks indicate differential DNA methylation patterns within the SV target region. P-values were calculated using a permutation test. (e) Proposed model of the epigenetic and transcriptional determinants associated with GFI1B enhancer hijacking in the RLsvz.