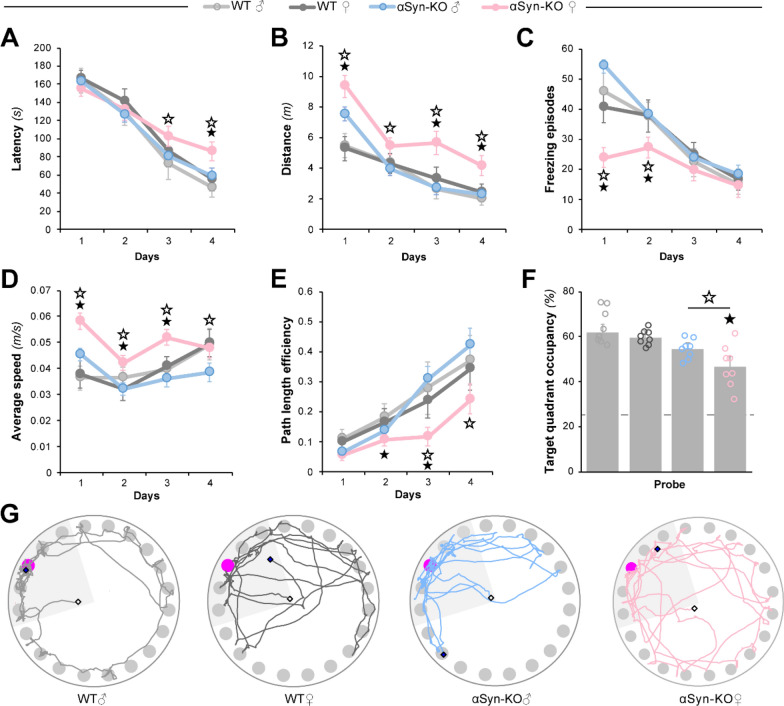
Fig. 4.
Genetic ablation of αSyn negatively impacts the performance of female mice on the Barnes circular maze. Male and female αSyn knock-out mice (αSyn-KO) and wild-type C57BL/6 J controls were tested in the Barnes circular maze (BCM) at six months of age. A, B Spatial learning of the BCM task was reflected by reductions in escape latency (A) and distance traveled (B). C, D Measurements of freezing episode numbers (C) and average animal speed (D) in the BCM task were used to assess phenotypic changes other than spatial learning. (E) Quantitative assessment of trajectories used by animals during the learning phase using path efficiency. (F-G) Spatial memory retention in the BCM task was determined by target quadrant occupancy (F) and by assessment of path traces (G). Data represent mean ± SEM; ★P < 0.05 compared to WT mice of the same sex, ☆P < 0.05 compared to mice of the same genotype and opposite sex, n = 8 mice/genotype/sex