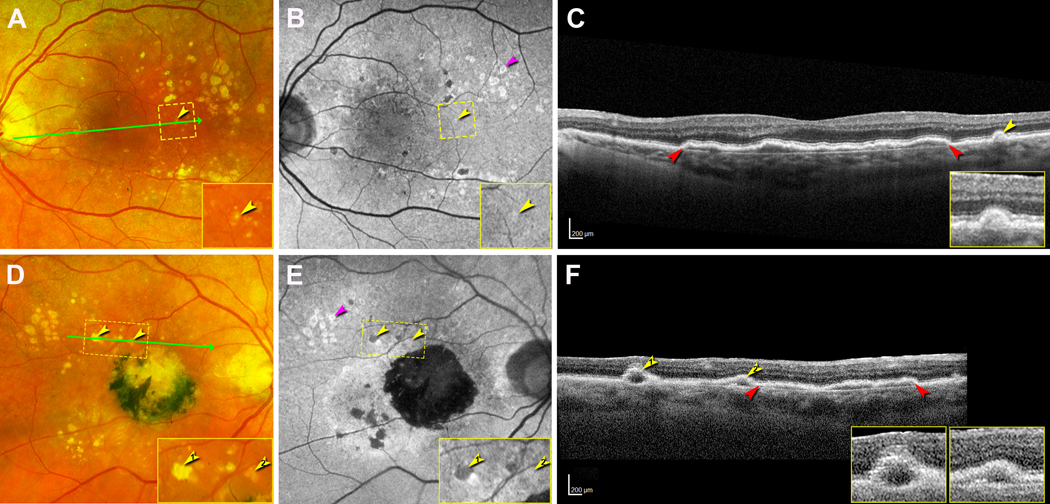
Figure 1. Multimodal imaging showing drusen at the last clinical visit.
All images were acquired 16 months before patient death. A, B, D, E were acquired with the Optos California. A-C. Left eye. A. Color fundus photograph (CFP) shows soft and refractile drusen that mostly spare the central macula. A small druse (yellow arrowhead) inside the yellow dashed frame is magnified in the inset. The green arrow indicates the location and direction of the corresponding optical coherence tomography (OCT) B-scan in panel C. B. With fundus autofluorescence (FAF) the small druse shows mild hyperFAF (yellow arrowhead, inset). A group of drusen have rings of hyperFAF around centers of hypoFAF (pink arrowhead). C. OCT B-scan shows an extensive shallow irregular retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) elevation (SIRE, red arrowheads), a small druse covered by RPE and overlying external limiting membrane (ELM) (inset). D-F. Right eye. D. CFP shows a central subretinal fibrosis with black pigment, and both refractile and soft drusen (yellow arrowheads, magnified in inset), mostly superior temporal to the fovea. The green arrow indicates the location of corresponding OCT B-scan in panel F. E. FAF shows the refractile druse to demonstrate hypoFAF and the soft drusen to show mild hyperFAF (yellow arrowheads, inset). A druse group has rings of hyperFAF around centers of hypoFAF (pink arrowhead). F. OCT B-scan shows two drusen (yellow arrowheads) on the left and SIRE (red arrowheads) on the right. Each druse has a hyporeflective core. The right druse is covered by RPE and ELM (insets). These bands are not visible over the left druse.