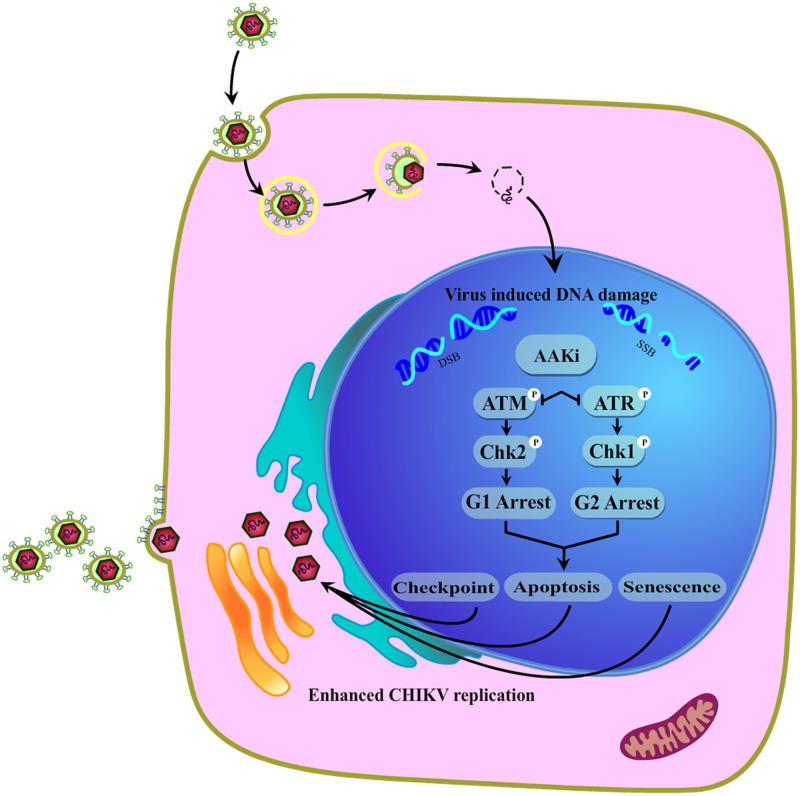
FIG 11.
Model portraying the modulation of the DDR pathways by the CHIKV infection. In the current investigation, it was found that CHIKV infection led to extensive DNA damage and stimulated both the ATM/Chk2 and ATR/Chk1 signaling pathways. Inhibition of the crucial host factors linked with DDR pathways caused a drastic reduction in the CHIKV infection. Additionally, it also led to cell cycle arrest in both the G1 and G2 phases, apoptosis, and senescence that further facilitated viral production.