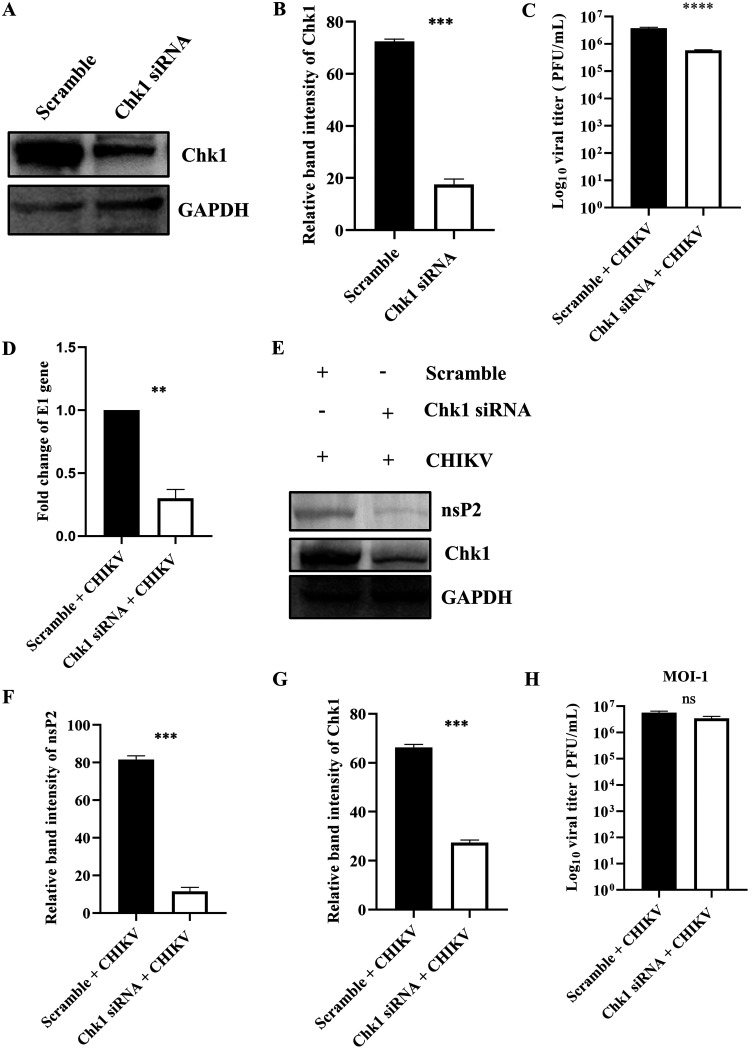
FIG 6.
Chk1 is crucial for CHIKV infection. The HEK293T cells were transfected with scramble siRNA or 60 pm of Chk1 siRNA. (A) Chk1 level was assessed by Western blotting, and GAPDH was used as a loading control. (B) Bar diagram displaying relative band intensity of Chk1 protein. After 24 hpt, cells were superinfected with CHIKV (MOI, 0.1) and harvested at 15 hpi for further downstream experiments. (C) Bar diagram representing the viral titer in the cell supernatant of scramble + CHIKV and Chk1 siRNA + CHIKV samples. (D) Bar diagram showing the fold changes of the E1 gene of scramble + CHIKV and Chk1 siRNA + CHIKV samples. (E) Western blot exhibiting the nsP2 and Chk1 protein levels after transfection and superinfection with CHIKV. (F and G) Bar diagrams depicting relative band intensities of the nsP2 and Chk1 proteins. After 24 hpt, cells were superinfected with CHIKV (MOI, 1) and harvested at 15 hpi for plaque assay. (H) Bar diagram representing the viral titer in the cell supernatant of scramble + CHIKV and Chk1 siRNA + CHIKV samples. Data of three independent experiments are represented as mean ± SD. The unpaired two-tailed Student’s t test was performed for all the experiments. **, P ≤ 0.01; ***, P ≤ 0.001; and ****, P ≤ 0.0001 were considered statistically significant. ns, not significant.